If you drive regularly, you know what it’s like to get stuck at a red light even when the road ahead is empty. Or you’ve probably crawled through traffic that clears up as mysteriously as it started. These pauses feel small, but across a day, and across a city, they add up fast.
When you look at how traffic actually behaves, these delays are easier to understand. Roads change minute by minute. Drivers switch lanes, pedestrians step into crosswalks, buses pull in and out, and a single ripple can slow everything down for a moment.
Most traffic systems, however, are not designed to react that quickly. Many still rely on preset signal timings and occasional manual checks, so they struggle when conditions shift in ways the plan didn’t anticipate.
To keep up, transportation systems have started paying closer attention to what’s actually happening on the road. Cameras placed at intersections, along highways, and inside vehicles don’t just record footage. They help systems monitor traffic flow, detect changes in real time, and respond more effectively.
This is enabled by computer vision, a branch of AI. By analyzing images and video, computer vision makes it possible for systems to recognize vehicles and pedestrians, track movement, and spot safety risks as they emerge.
Computer vision is making a difference in urban transportation. (Source)
Cities using computer vision in transportation systems are already seeing results. Some smart traffic systems have reduced travel time by up to 25% by making better decisions based on real-time road conditions.
In this article, we’ll explore how computer vision in transportation is helping cities better understand what’s happening on their roads, respond to changing conditions in real time, and build systems that are safer and more efficient.
Traffic rarely breaks down all at once. It usually begins with something small, like a slow-moving intersection or a vehicle stopped where it shouldn’t be. When these moments go unnoticed, delays spread quickly and affect roads far beyond where the problem started.
Computer vision lets traffic teams notice these changes early. By analyzing live video from intersections and busy roads, it turns camera footage into a clear view of how traffic is moving across connected streets. This makes it easier to understand where pressure is building and where action is needed before congestion grows.
With this visibility, traffic systems can respond as situations develop. Signal timings can be adjusted, traffic can be redirected, and incidents can be flagged as soon as they occur. Instead of reacting after delays have already formed, cities can take steps while traffic is still flowing.
A good example of this approach in action is Hangzhou, China. The city uses computer vision to connect live road data across its network, coordinating traffic signals and speeding up incident response. Instead of treating each intersection as its own island, it manages traffic as one connected system, keeping vehicles moving smoothly and response times short.
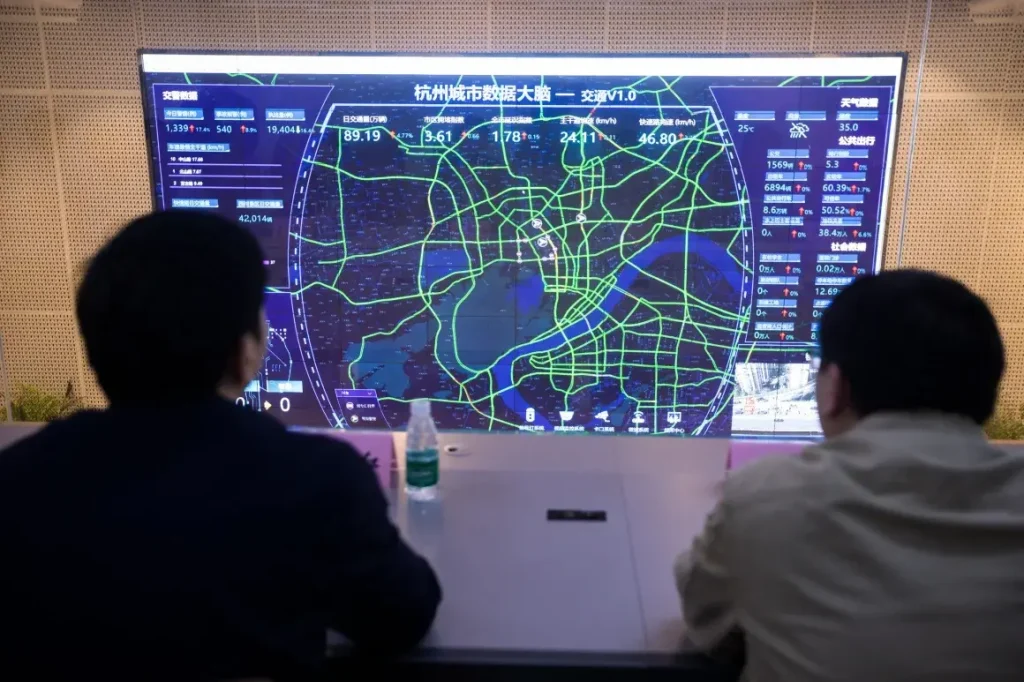
Traffic in Hangzhou has improved, thanks to AI. (Source)
So, how does traffic footage become actionable data? Computer vision solutions can analyze videos frame by frame to detect road users, track movement over time, and estimate what is happening on the road.
Here are a few common computer vision techniques used in smart transportation systems:
For decades, traffic systems have relied on fixed rules. Computer vision is changing that approach. AI-driven transportation systems respond to what’s actually happening on the road, moment by moment.
You can see the shift most clearly at smart intersections. Instead of running on preset timing plans, the signals adjust to what is happening in real time.
They respond to vehicle volume, pedestrian movement, and growing queues, reducing unnecessary waiting and keeping traffic moving more smoothly. For example, in Pittsburgh, the AI-based Surtrac system demonstrated this by reducing travel time by 25% and cutting vehicle waiting time by 40%.
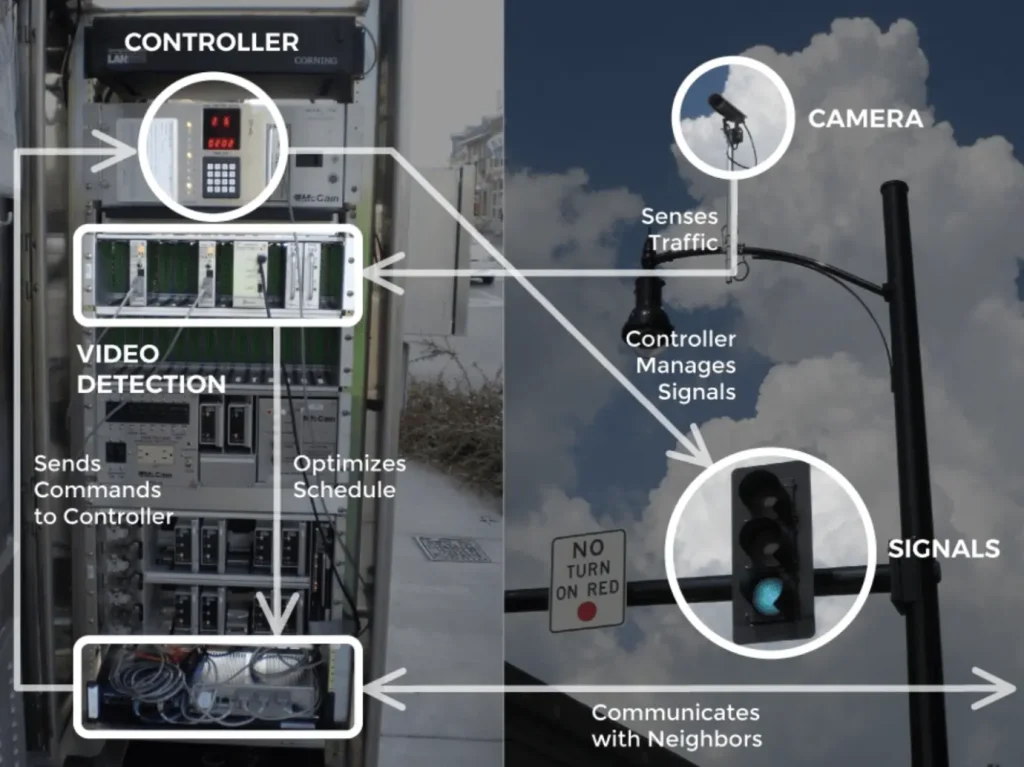
How Surtrac Works (Source)
In fact, the impact of computer vision in transportation goes well beyond individual intersections. Across cities, computer vision is being integrated with traffic signals, control centers, and connected vehicles, allowing traffic to be managed as a coordinated system instead of isolated points.
This level of coordination comes from combining computer vision with IoT sensors, edge AI, and 5G. Together, they can speed up incident responses, improve traffic flow, and give emergency vehicles priority. Less idling also reduces fuel use and emissions.
Now that we’ve seen how computer vision is changing transportation, let’s look at how it’s being used on real roads.
Congestion often begins at intersections. When signals run on fixed schedules, they keep cycling even as traffic shifts, and cars pile up simply because the timing doesn’t match what is happening on the road.
Cities are responding with smart signals powered by computer vision. AI-enabled cameras measure vehicle density, queue length, and movement, then adjust signal phases as traffic builds or clears.
When lights respond to real conditions, backups can be eased before they spread. Drivers spend less time waiting at red lights, traffic moves more evenly, and stop-and-go driving drops. The payoff is not just shorter trips, but lower fuel use, fewer emissions, and cleaner air.
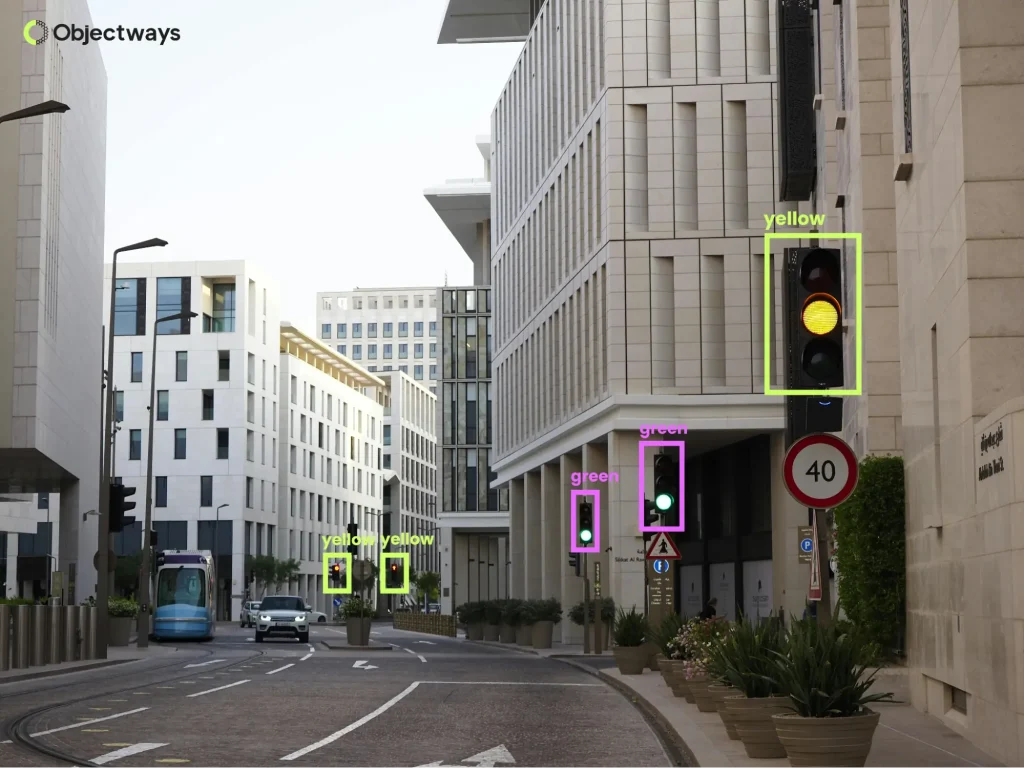

Traffic signals can also be monitored with the help of computer vision.
Dubai is an interesting example of this. The Roads and Transport Authority has deployed an AI-driven traffic management system that combines computer vision with connected infrastructure to coordinate signals using live video. The system is expected to reduce congestion by up to 37%.
Road safety challenges often start with brief lapses in attention. It could be a tired driver behind the wheel or a pedestrian stepping into traffic. Improving safety depends on recognizing these risks early and responding before accidents occur.
Computer vision supports this by monitoring behavior inside vehicles and on the road. In the cabin, driver monitoring systems track cues like eye movement, head position, and posture to spot fatigue or distraction and trigger real-time alerts before it becomes dangerous.
Meanwhile, cameras facing the road can detect hazards in real time, such as pedestrians entering a crosswalk, vehicles drifting out of lane, or sudden stops that signal a developing incident.
These capabilities are already being integrated into advanced vehicle systems. For example, Waymo’s autonomous vehicles rely on computer vision to detect pedestrians and cyclists in real time. Waymo reported that, compared with human-driven benchmarks, its driverless vehicles were associated with 92% fewer pedestrian injuries in the scenarios it analyzed.
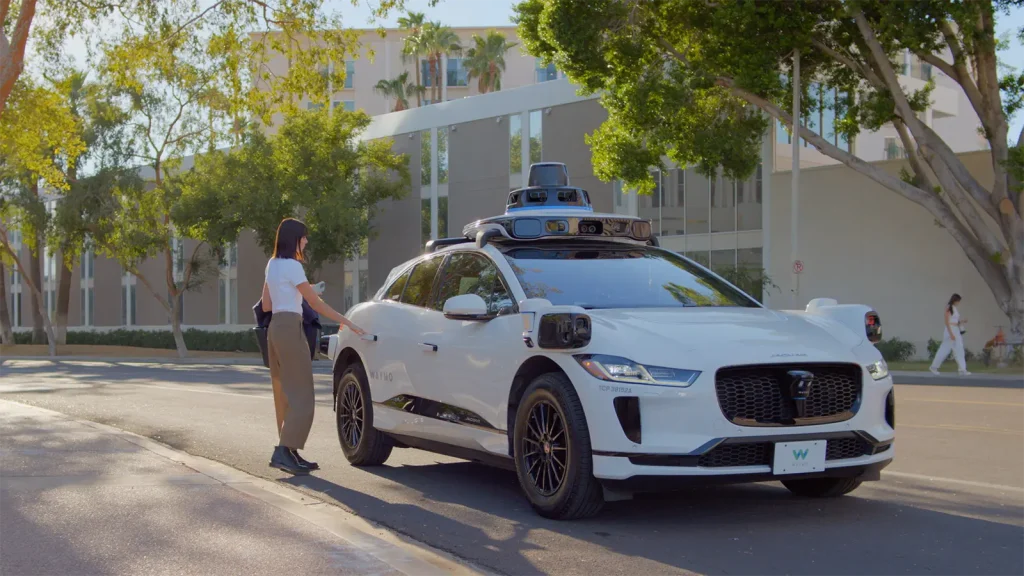

A Look at Waymo’s Robotaxi (Source)
Roads usually wear down slowly. Small cracks turn into potholes, and lane markings fade over time. The problem is that many cities still check road conditions on a schedule, often by hand, so issues can go unnoticed for weeks or months.
Computer vision changes that by making road checks more continuous. Cameras on city vehicles, roadside units, or drones capture street-level images as they move through the network. AI models trained on examples of common defects can then scan new footage to spot potholes, surface damage, faded lane lines, and missing signs.
When something is flagged, the system can generate a geo-tagged report so crews know exactly where to go and what needs attention. That makes it easier to prioritize repairs based on severity instead of relying on occasional inspections.
San Jose, California, has tested this kind of approach through a road safety pilot program that uses street imagery to identify problems more efficiently. With earlier detection and clearer priorities, cities can fix issues sooner, improve safety, and use maintenance budgets more effectively.

A Glimpse into San Jose’s Road Safety Conditions Pilot Program (Source)
Computer vision is helping transportation systems improve safety and manage traffic more efficiently. Here are some of the key benefits it brings:
While computer vision offers significant advantages, it also comes with challenges that need to be addressed. Here are some key limitations to consider:
Overcoming these challenges depends on strong data foundations. Access to high-quality, well-annotated visual data is critical for building reliable systems.
At Objectways, we make things simpler by providing high-quality data annotation and labeling, so transportation AI systems can work reliably in real-world conditions.
Computer vision in transportation uses images and video to measure what is happening on the road, such as where vehicles and pedestrians are, how traffic is moving, and when something unusual occurs. That makes it easier for cities to adjust signals, detect incidents sooner, and monitor safety without relying only on periodic manual checks. It still works best with clear human oversight, since the system’s output needs validation and context.
When these models are trained on high-quality data and deployed with responsible AI practices, they can support faster decisions while preserving privacy and accountability. Cities that get this balance right can respond sooner, plan more effectively, and improve safety at scale.
Ready to build reliable computer vision solutions for transportation? Connect with Objectways to power your AI systems with accurate data annotation, domain expertise, and responsible deployment.
