Nowadays, artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a key role in how many organizations operate. In fact, recent surveys show that over 70% of enterprises are already using AI in at least one of their core business functions, ranging from analytics to automation.
This year, AI trends have reached a point where they have moved from experimentation to everyday business workflows. For instance, many banks today use AI to flag fraud during transactions, while hospitals apply AI-assisted imaging to support clinical decisions. Similarly, manufacturers are also deploying AI systems to inspect products on production lines.
Other than these industrial use cases, AI itself is also progressing. Modern AI models are able to work with multiple data types such as text, images, audio, and video. This means organizations can build AI applications that better understand their data and information. In parallel, enterprise investments in AI are also expected to keep growing in 2026. Many organizations are allocating budgets toward automation tools and internal AI infrastructure for long-term use.
In this article, we’ll explore the key AI trends of 2026 and see how technology adoption and real-world use are shaping businesses, developers, and entire industries. Let’s get started!
Before we dive into the details, let’s take a quick look at where AI is trending in 2026, including agentic AI systems, physical AI and robotics, and AI as an enterprise operating layer.
Agentic AI refers to systems that autonomously take actions, adapt to changes, and manage workflows. One example of this is the enterprise platform Agent5i. The platform integrates autonomous AI agents to automate planning and decision workflows across complex business systems, including cloud and hybrid environments.
Such AI agents can also handle multi-step tasks within structured workflows. This makes them very reliable for real-world use cases such as autonomous ticket management, automated marketing content assembly, and AI-driven document orchestration.
These applications are built based on ongoing research in AI agentic systems. For instance, research projects like the fully autonomous agent, Manus AI, show how AI can manage complex tasks with limited supervision, providing a foundation for many independent systems.
As these capabilities evolve, many enterprises are incorporating AI agents into their internal workflows. They trigger actions, evaluate outcomes, and coordinate between different systems, allowing teams to focus on what’s important, like reviews, rather than intervening at every step.
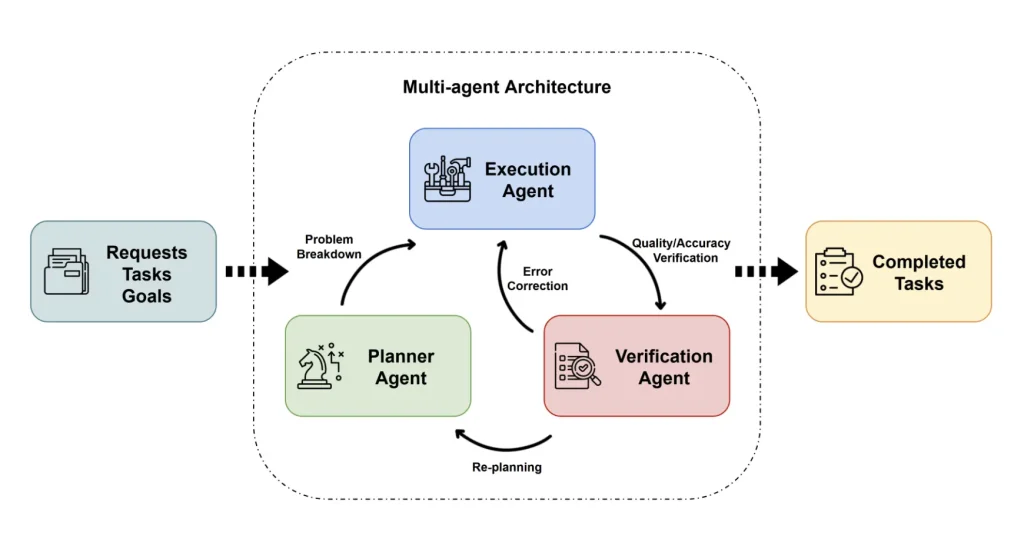
Manus AI’s Multi-Agent Architecture For Autonomous AI Systems (Source)
Physical AI brings intelligence to robotic machines that can see, move, and act in the real world. These robotic systems can use data from sensors and cameras to understand their surroundings and adjust their actions based on movement, obstacles, and the task at hand.
For example, Amazon has deployed over 1 million AI-driven warehouse robots globally. And its new DeepFleet foundation model improves coordination across the robotic fleet to increase efficiency and reduce delivery times.
In particular, Amazon’s Vulcan system is a great example of such robots. They can precisely handle inventory and are already operating in distribution centers in the U.S. and Europe. Similarly, Google DeepMind’s Gemini Robotics models are powering robots with vision-language-action capabilities, enabling them to interpret complex environments and perform tasks beyond basic motion.
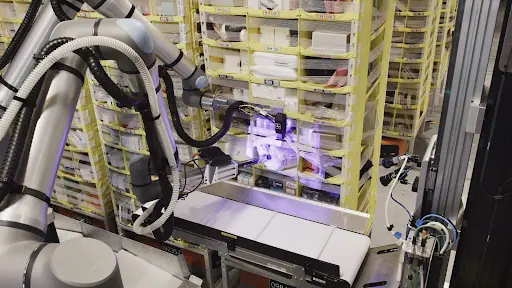
Vulcan Using a Vision Guided Picking Arm (Source)
Today, many organizations include modern AI capabilities in their existing core enterprise systems rather than treating them as separate tools. This can be done by partnering with AI solution providers to create enterprise AI platforms and agents built specifically for an enterprise’s operations.
According to industry analysis, about 40% of enterprise applications will include AI agents that execute tasks and workflows as part of core systems by the end of 2026. These enterprise AI platforms help teams deploy AI into existing systems such as CRM, ERP, and HR software. This makes it possible for organizations to make decisions, automate responses, and manage business logic using modern AI tools.
For example, Snowflake’s $200 million partnership with OpenAI embeds advanced AI models into its cloud data platform. This enables organizations to automate complex tasks directly within secure enterprise environments.
Innovations in AI infrastructure are becoming an important AI trend in 2026. In fact, the AI Infrastructure market is expected to grow to $394.46 billion by 2030. For instance, investments in compute power, edge deployments, and data platforms help enterprise teams support real-time use cases and scale workloads across business functions.
In many cases, cloud platforms are a foundation for AI workloads, and companies are partnering up to keep up with AI demand. In late 2025, OpenAI signed a $38 billion cloud computing agreement with AWS to secure large-scale compute for training and running advanced AI models, including GPT, and for autonomous systems.
While many prefer cloud infrastructure for their AI needs, others prefer edge solutions that run AI systems on-site without the cloud. Since edge systems are closer to data sources, they can easily handle real-time workloads and reduce latency.
Cisco’s “Unified Edge” platform is a great example. It is designed to run AI workflows locally in retail stores, factory floors, and healthcare sites.
Similar to organizations, entire governments of countries are also investing in AI infrastructure for the future. India, for example, continues to invest in domestic AI infrastructure through initiatives such as Dell and NxtGen’s AI factory, which features over 4,000 NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs. This is to support local AI development and reduce reliance on foreign resources.
These AI infrastructure trends in 2026 are helping power applications that require both scale and real-time responsiveness.
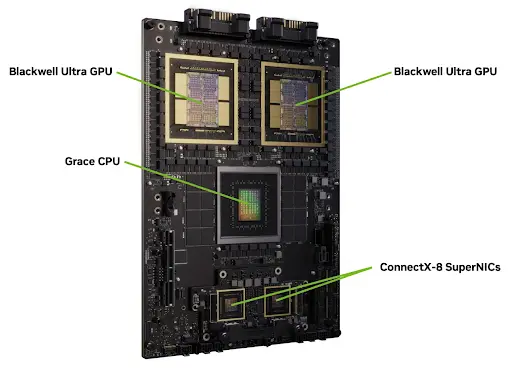
A Look at NVIDIA’s Blackwell Ultra Chip (Source)
In 2026, large enterprises across different industries are adopting AI directly into daily operations. Here are some popular industries adopting AI:
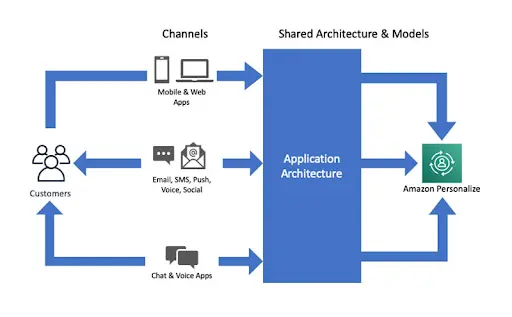
Amazon Enterprise AI Architecture For Omnichannel Personalization (Source)
These real-world deployments show that AI is now a core part of business infrastructure, not just an experimental add-on. Companies are building their processes and systems with AI in mind from the start, rather than treating it as something extra.
Now that we have a better understanding of AI adoption trends in 2026 across industries, let’s take a closer look at how they could affect workforce jobs and skills.
AI continues to influence how work evolves across industries by redesigning jobs and creating new AI-centric roles, enabling people to work alongside AI systems in daily operations. In fact, AI and automation could influence close to one-third of work activities by the end of the decade. Such a change increases the value of roles that combine technical understanding with business and domain knowledge.
Machine learning engineers are a great example. They concentrate on building and maintaining AI models in production environments. Roles like data scientists focus more on interpreting model outputs and connecting insights to real business decisions. AI product managers, on the other hand, play a growing role by shaping how AI systems fit into workflows while balancing performance, usability, and risk.
Moving past 2026, we can also expect a rising demand for professionals with hybrid skill sets. These are professionals who have a combined understanding of data, AI systems, and how a business works in an organizational context.
As more and more AI systems are used for decision-making by different organizations and governments, there will be a greater focus on safety, accountability, and responsible use. Ethical considerations now influence how AI systems are designed, deployed, and governed in 2026.
One of the major drivers of this trend comes from AI regulation. For example, the European Union’s AI Act introduces clear risk-based categories for AI systems, with stricter requirements for high-risk use cases such as healthcare, finance, and biometric identification. These rules push organizations to document models, manage data quality, and ensure human oversight.
Such regulations are popular and trending in 2026 due to growing concerns about AI-driven misinformation. In fact, according to the World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report, AI-generated misinformation and disinformation rank among the top global risks due to their impact on public trust, elections, and social stability.
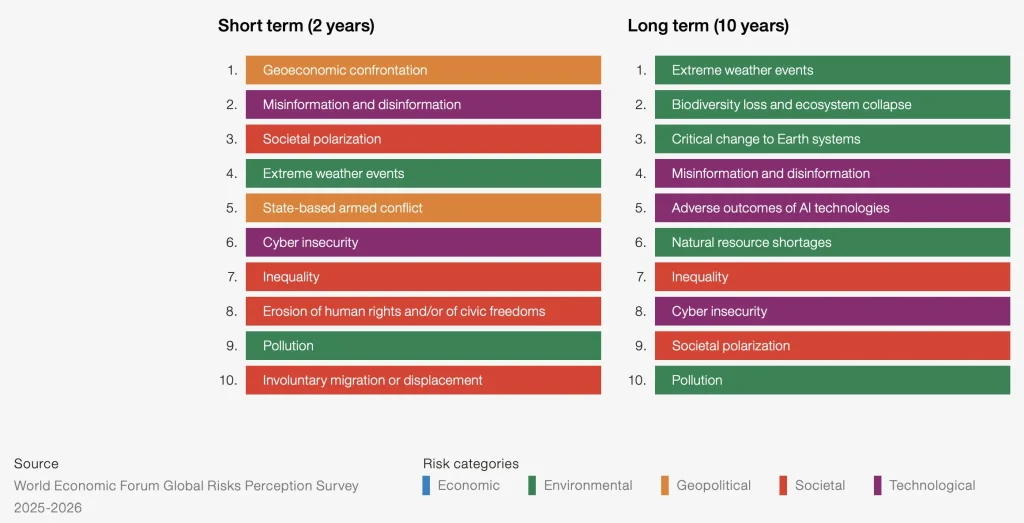
Global Risk Trends In 2026 (Source)
These misinformations are a result of poor AI models trained on biased data. This is also an area receiving a lot of attention. Studies cited by organizations like NIH show that biased training data can lead to unequal outcomes in hiring, lending, and law enforcement systems, prompting calls for stricter evaluation and auditing practices.
Enforcing rules and laws regarding AI transparency is crucial to reducing AI misinformation and bias and increasing trust in AI. By 2026, organizations that prioritize AI transparency and trust practices are set to see significantly higher adoption and user confidence compared to those that do not.
AI is becoming an important part of how consumer hardware operates by default. Many companies are using edge devices to run AI systems locally to respond faster and handle personal data more carefully.
For instance, at the CES 2026 consumer technology showcase, companies showcased consumer hardware that learns and adapts to home environments. For example, LG presented its CLOiD home robot, which can coordinate with household appliances and perform routine tasks autonomously inside the home.
Similar to LG, SwitchBot introduced the Onero H1 humanoid assistant, which can organize laundry and prepare simple meals. These demonstrations showed how AI systems are combining perception, planning, and action within real living spaces, which is a key AI trend in 2026.
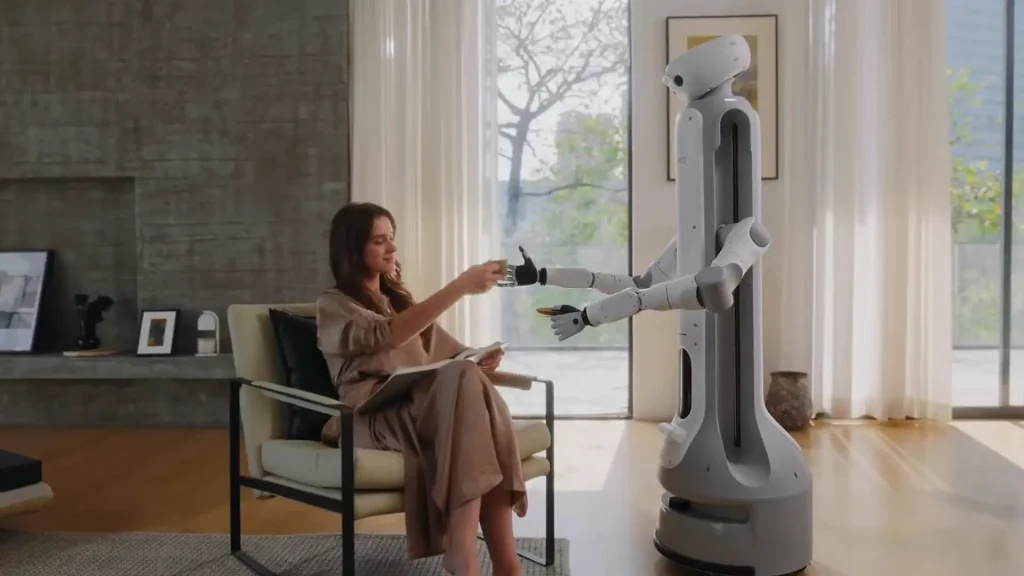
Onero H1, a humanoid assistant, performing everyday tasks inside a home. (Source)
The AI trends of 2026 point toward more global adoption, investment, and higher use of AI systems in the years ahead. AI tools like generative AI could add between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy. These trending AI tools can improve productivity across industries such as customer operations, software development, and research.
Many software companies will also adopt various AI tools in the coming years. In fact, by 2028, at least 75% of enterprise software engineers will use AI coding assistants, reflecting how AI is getting embedded in everyday development workflows.
Ongoing research in multimodal models, autonomous systems, and AI safety shapes how these systems evolve beyond 2026. As adoption grows, organizations are placing greater emphasis on reliability, governance, and long-term value from AI deployments.
2026’s AI trends show how artificial intelligence is becoming part of everyday systems and real-world operations. Agentic AI, physical AI, and enterprise adoption are now guiding how teams build and use AI at scale. With the right preparation, governance, and integration, organizations can turn these trends into lasting value.
Looking to build reliable AI systems backed by high-quality data? Need support with data collection, annotation, or domain-specific labeling? At Objectways, we help teams create strong data foundations for real-world AI. Contact us to get started.
