As of 2025, there are more than 5.6 billion social media users worldwide. On social media platforms such as TikTok, people upload nearly 117 million videos every day, equivalent to over 4.9 million uploads per hour. A single post can travel across platforms within seconds, and a short video or an image can shape public opinions before anyone has time to verify its origin and authenticity.
For instance, in June 2024, a video of Nigel Farage, a well-known political figure in the United Kingdom, circulated during the general election campaign. The clip showed him inside a video game, and it looked pretty convincing, but the event never happened. It was generated with an artificial tool, and it moved quickly through social networks before the truth became clear.
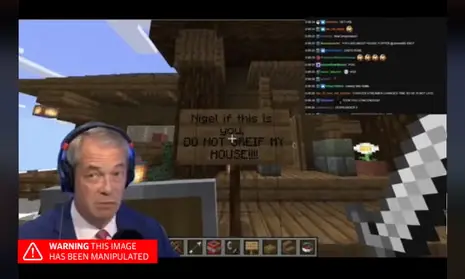
An Example of a Frame from a Deepfake Video (Source)
With incidents like this becoming more common, many people are now asking what is content moderation and why platforms rely on it to manage risks at scale. In fact, the European Digital Services Act and several regional policies now require platforms to review how they detect risk and use different types of content moderation.
At the same time, user activity continues to grow at a pace that exceeds the capacity of any human review team. Platforms now depend on automated content moderation systems to handle the volume of content they are handling and rely on human reviewers to interpret context when decisions require a deeper look.
In this article, we’ll explore how content moderation works and how each component of a content moderation pipeline works together to keep platforms safe. Let’s get started!
Before we explore the details, let’s discuss what is content moderation in the context of today’s fast-moving digital platforms.
Content moderation involves reviewing and guiding the flow of user-generated content to ensure online spaces stay safe, welcoming, and predictable. It works like a set of quiet guardians in the background. They review text, images, video, and audio to see whether the content fits the rules of a platform and the expectations of a community.
You can spot content moderation all around you online. A comment exposing private details might disappear, and product photos are checked before going live in a marketplace. These behind-the-scenes steps help ensure the right content reaches the right audience at the right time.
Here are a few important reasons why moderation matters today:
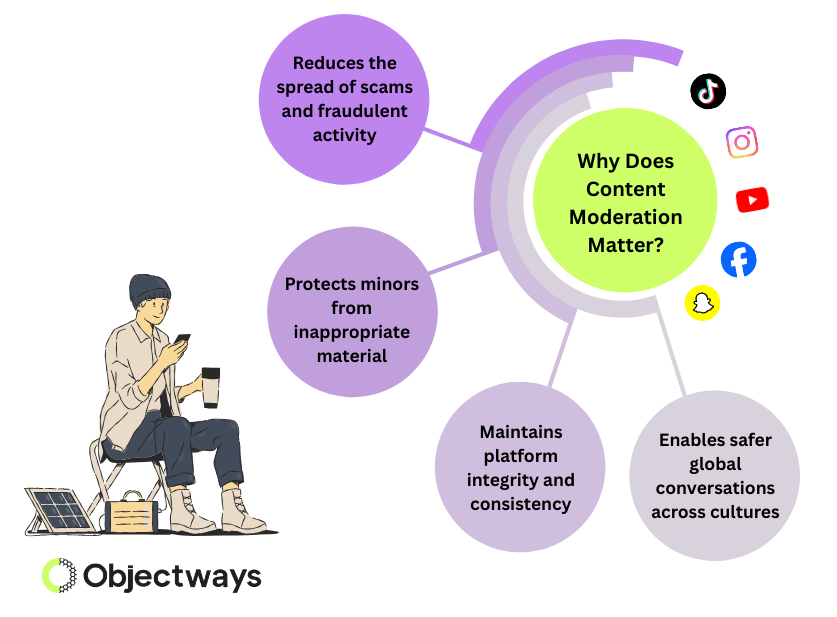
What Is Content Moderation and Why Does it Matter?
Once you know what is content moderation at a basic level, the next step is understanding how a modern moderation pipeline actually works behind the scenes.
Content enters a moderation system in different ways, and each route shapes how the system begins its work. Some platforms receive a steady stream of real-time uploads from users who post throughout the day. Others process content in scheduled batches, which is common among enterprise teams that gather information over longer periods.
Meanwhile, certain systems also perform background scans to review older content when policies change or when new rules come into effect. All of these sources typically feed into the same pipeline to evaluate content consistently.
Once a piece of content arrives at the content moderation system, ingestion begins. This step confirms the content type and performs basic checks so that the rest of the system knows how to handle it.
The next stage prepares the content. Text is cleaned, images are formatted, and video or audio files are arranged so that automated tools can read them correctly.
After preparation, automated analysis begins. Models scan the content for signals, such as harmful language, unsafe imagery, or risky audio cues, and assign a score indicating how closely it follows platform rules. This score determines the next step: the content may be approved automatically, sent to human review, or removed if a clear violation is detected.
The final stage records the decision and stores helpful metadata. These records support audits and guide future policy updates. This automated moderation pipeline provides the foundation for the more advanced systems that we’ll discuss next.
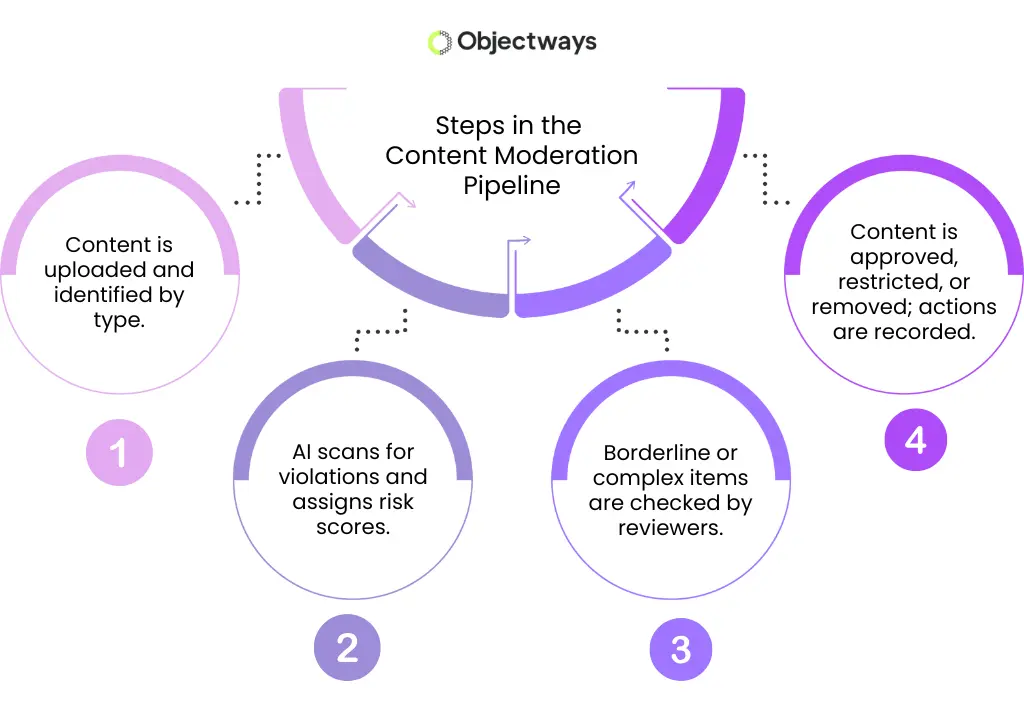
Overview of the Content Moderation Process
Generally, a content moderation pipeline has to work across many formats because users share content in various ways. For instance, text conveys meaning through language, images rely on visual detail, videos add motion and sound, and audio carries tone and intent. A dependable system needs to make sense of each format while applying a consistent standard across all of them.
Content moderation systems also need to operate at scale. Large platforms process thousands of items every minute, so the models powering automated moderation have to perform consistently. When throughput slows, backlogs grow, and users notice the delay.
In addition to this, a unified scoring system helps the pipeline make decisions quickly. Scores places content into clear zones that show whether an item can pass through, needs a second review, or requires removal.
Here’s a quick glimpse of other key constraints in designing a moderation pipeline:
When you scroll through social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, or YouTube, you come across all kinds of content. You might read a text post, swipe past a photo, watch a quick video, or listen to a short audio clip.
Each of these formats communicates meaning in its own way. Because of this variety, automated content moderation has to understand each format a little differently. It also has to account for other factors, such as explainability, multilingual content, cultural nuance, and how context can change the meaning of a message or image.
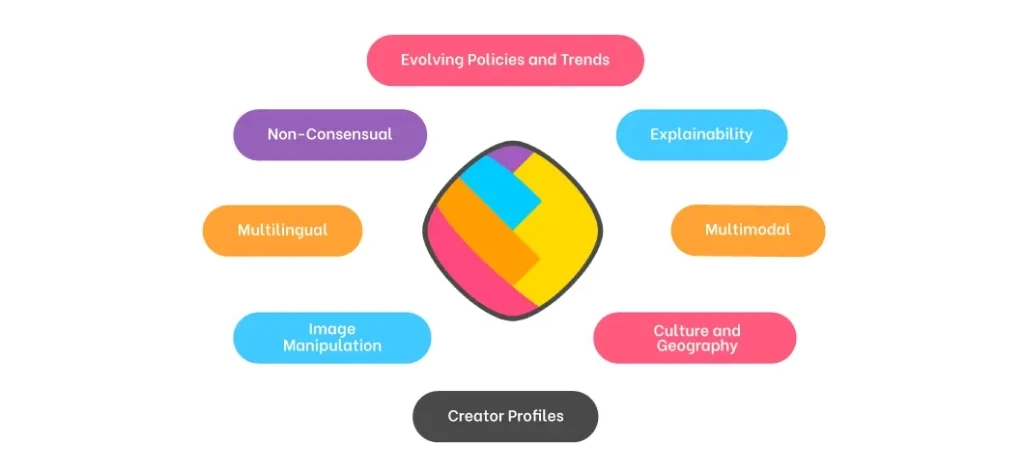
Factors That Make Different Types of Content Complex to Analyze and Moderate (Source)
Next, let’s walk through the main types of content moderation and how automated tools make sense of each one.
Processing text for moderation begins with a few preparation steps. The system identifies the language, separates sentences, and breaks long passages into smaller parts. Once the text is organized, automated content moderation tools can study its meaning more effectively.
The system then looks for details that may require attention. It may check for private information such as names or contact details, or look for emotional shifts in a message that could change how it should be interpreted.
Text can be surprisingly nuanced. A sentence that sounds encouraging in one conversation may feel uncertain in another. Culture, region, and evolving expressions also influence how a message should be understood. These factors make text moderation a challenging task for automated systems.
Consider a situation where a social media platform updates its policies and suddenly needs to review millions of images. To handle this kind of volume, image moderation relies on several computer vision models working together.
Object detectors help identify items that appear in the scene, image classifiers sort the image into broader categories, and safety-focused models are trained to spot sensitive or high-risk content. Each model contributes specific insights.
For example, an object detector might find a weapon or alcohol bottle, while a safety classifier might flag nudity or graphic content. The system then brings these outputs together to create descriptive labels and confidence scores that indicate whether the image may violate platform rules.
Even with these tools, images can be difficult to interpret. A sports photo might look intense even if nothing unusual is happening, and a medical training image can seem alarming without context. These examples show why image moderation requires thoughtful interpretation. The system has to consider what the models detect and how those detections might be understood by different viewers.
Videos add an extra layer of complexity because they involve continuous movement. To handle this, automated systems break a video into frames or segments so each moment can be analyzed. This matters because a significant event may appear for only a second.
In addition to movement, videos include sound and frequent scene changes, which create more signals for the system to evaluate. Many videos also contain on-screen text or small graphic elements that need separate attention.
Because a video can contain thousands of frames, a video content moderation system must balance accuracy with efficiency. Reviewing every frame delivers the most detail but slows processing, while sampling frames is faster but can miss brief moments. Each platform chooses the approach that best fits its performance and accuracy needs.
Audio starts out as raw sound, so the first thing automated moderation systems do is turn it into text using speech-to-text models. This makes the content easier for language tools to understand and also allows the system to pick up on tone or emphasis once the words are mapped out.
But audio brings plenty of challenges. Background noise can make it hard to hear. People might switch between languages or use phrases that only make sense because of the way they’re said. And sometimes a clip is only a few seconds long but still carries meaning that depends heavily on context. All of this makes audio one of the more dynamic and tricky formats for automated systems to analyze.
Automated content moderation can process huge volumes of material far faster than any human team, but some situations still need human judgment. Meaning often depends on context, and that context can change how a phrase, an image, or a short clip should be interpreted. While automated systems look for patterns in the data, human reviewers can consider intention, purpose, and the environment in which the content appears.
A recent example shows how important this distinction is. In October 2023, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, several health organizations posted educational visuals demonstrating self-exams. These posts were mistakenly removed because the system focused on the surface details of the images. The content was later restored once human reviewers recognized its value for public health education.
Human reviewers play a crucial role in these types of situations. Their decisions help refine scoring thresholds and guide future model updates. This feedback loop makes it possible for automated systems to improve over time and keeps the overall moderation process accurate and reliable.
Human reviewers make up the interpretive layer of a moderation system. When automated tools reach their limits, reviewers step in to apply context, nuance, and real-world judgment.
So, what does this look like in practice? Content enters structured queues based on type or urgency, creating an organized workflow. Reviewers then work through an interface that brings together everything they need: the content itself, the model’s prediction, relevant metadata, and the policy notes that apply. This helps them understand why the system flagged the item and what to consider next.
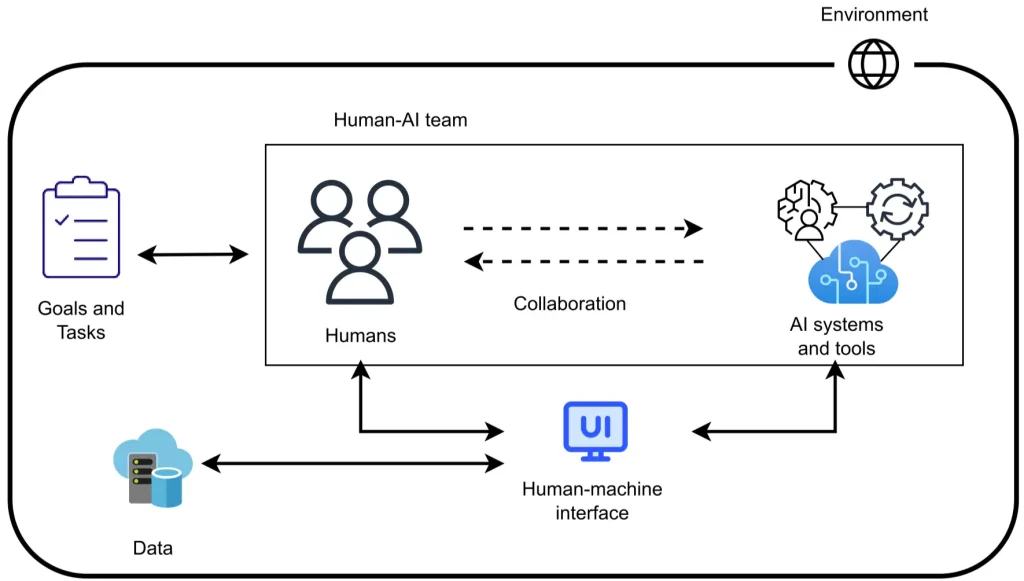
Human-AI Collaboration Strengthens Content Moderation Workflows (Source)
Once they review the content, they choose a clear action. They can approve it, reject it, or request clarification if something is unclear. Some items are escalated to senior reviewers when additional expertise is needed. Every decision is logged to support audits and quality checks, and teams track metrics like accuracy, decision speed, and escalation rates.
Reviewer well-being is also an important part of the process. Teams rotate assignments and provide support resources, recognizing that thoughtful review requires a healthy and steady environment.
As content volume grows, moderation teams face a range of technical and operational challenges that require careful planning. Here are some of the key areas that need special attention when designing a scalable moderation pipeline:
At Objectways, we offer a moderation pipeline built to handle the scale and complexity of modern user-generated content while keeping decisions accurate and consistent. Our system applies a unified set of policies across text, images, video, and audio, ensuring every format is evaluated with the same standards.
Each item receives an automated score based on outputs from multiple AI models, including LLMs, vision models, automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, and safety classifiers. This score determines the next step in the workflow.
Clear cases are processed automatically, while borderline content is routed to human reviewers who interpret intent, nuance, and context. When a case requires deeper analysis, it moves to a senior review layer where experienced reviewers provide final judgment. This tiered setup enables automated moderation to run efficiently while still relying on human expertise when needed.
Our moderation pipeline is built on a serverless, modular architecture that scales automatically as content volumes change. Each content type moves through its own dedicated processing path, so text, images, video, and audio receive the appropriate analysis. Cloud-based services handle language processing, image moderation, video inspection, and audio transcription.
Eventually, every path feeds into a unified decision layer. This design keeps automated moderation efficient while allowing the system to account for the unique challenges of each content format.
We also separate information clearly across different storage areas. Raw content is stored in one location, automated outputs, such as labels and scores, are stored in another, and human review decisions are recorded separately. This structure improves clarity, supports compliance, and makes it easy to trace how each item moved through the pipeline.
Simply put, lightweight databases capture labels, decisions, and timestamps, giving teams a complete historical record. Continuous monitoring and logging help maintain reliability, while core AWS services provide the compute, storage, and analytics needed to scale the pipeline smoothly.
We’re thrilled to invite you to an upcoming webinar in the second week of January, where we’ll walk you through how modern platforms manage content moderation at scale.
This live session features real-world examples and a complete multimodal moderation workflow built with Amazon A2I. You’ll see exactly how automated tools and human reviewers work together to evaluate text, images, audio, and video with accuracy and consistency.

Don’t Miss Our Webinar on Content Moderation!
We’ll take you behind the scenes and show how ingestion pipelines, model orchestration, and reviewer workflows all connect inside a single, unified architecture. You’ll also get a guided look at our QuickSight dashboard, where teams can explore label distributions, reviewer agreement, performance trends, and more.
Whether you’re curious about how these systems operate in practice or interested in how Objectways builds scalable moderation pipelines on AWS, this session is the perfect place to start.
Stay tuned – final dates and registration details will be posted on the Objectways LinkedIn page soon. We’d love to have you join us!
Modern content moderation relies on multiple layers that work together, starting with automated analysis and supported by human review when deeper context is needed. Scalable systems must handle large volumes of text, images, video, and audio while still making decisions that are consistent and timely.
A reliable pipeline also keeps clear audit records, protects sensitive information, and adapts to changes in language and culture. Serverless and distributed designs help teams handle traffic spikes smoothly, while human judgment remains essential for interpreting nuance and improving model performance over time.
If your organization is looking to build or enhance its content moderation systems, Objectways is here to help. We offer end-to-end content moderation services that include workflow design, data operations, reviewer management, and fully managed human review teams.
Whether you need support with automated pipelines or hands-on moderation, our team can help you create a safer and more reliable content experience. Contact us to discuss your goals and learn how we can support your content safety efforts.
