Sometimes, healthcare can feel like a puzzle. Every patient’s condition, treatment, and outcome is a unique piece. To make the best decisions, every piece counts – and that’s where health data comes in.
Health data refers to the information found in an individual’s medical records and overall health, as well as data gathered from groups of people. It includes details like diagnoses, treatments, lab results, and other key health indicators. Analyzing this data is crucial for making informed medical decisions in healthcare. More importantly, collecting and processing this data in real-time is vital for improving patient care.
With so much data generated every day, artificial intelligence (AI) and wearable sensors have become more common in healthcare. Such technologies make things easier for patients and doctors by handling tasks faster and at a lower cost.
For example, remote patient monitoring systems use wearable biosensors to track vital signs in real-time, helping healthcare providers spot issues early. Similarly, Internet of Things (IoT) devices like smart glucose monitors and connected blood pressure cuffs gather data that AI models can analyze to detect trends and customize treatments.
As a matter of fact, many healthcare centers are already using AI for different applications. Surveys show that 86% of healthcare companies are using AI, and the global AI in healthcare market is forecasted to expand by 38.5% annually from 2024 to 2030.
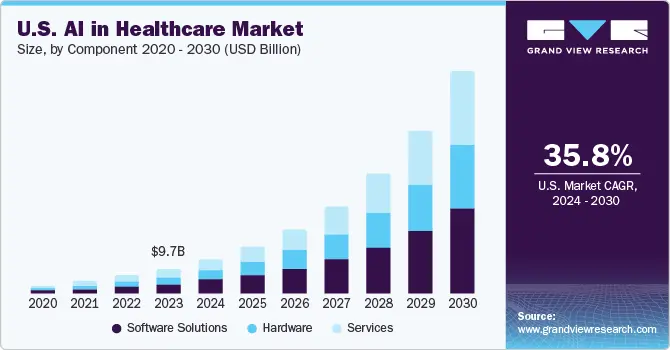
The AI in Healthcare Market (Source)
In this article, we’ll explore how wearable biosensors and AI are being used to enhance patient care. Let’s get started!
As the population grows, healthcare centers are being challenged with monitoring and assisting more patients. Interestingly, IoT-based biosensors in smart wearables are being used to enable real-time health tracking to catch issues early. These devices have evolved from simple step counters to tools that predict diseases and enhance overall health. They are quickly becoming a rising trend in personal healthcare.
The main goal of these wearable biosensors is to help users monitor their health and get timely alerts if something is wrong. These sensors can also let people track their health anytime, anywhere, using mobile apps without needing to visit a clinic. Doctors and medical professionals can also use the data from these devices to make quicker and more accurate diagnoses, saving time for everyone.
For example, a study by the Stanford University of Medicine shows that wearable sensors similar to Google’s Fitbit can be used to track and gather health data related to heart rate, daily activity, skin temperature, and more. Analyzing this data can provide insights into health issues like infections, inflammation, and insulin resistance. The study explained that by setting a baseline for each person, these sensors can help detect unusual changes linked to environmental factors or health problems. Going a step further, AI algorithms that recognize these patterns can help improve medical diagnoses and research.

Smartwatches are a common type of wearable sensor nowadays. (Source)
Internet of Things devices are changing the face of healthcare. They can be used to collect and share a patient’s health data in real-time. They also give doctors a clearer picture and reduce uncertainty in diagnosis and treatment.
Specifically, by analyzing large amounts of health data, these devices can be used to predict patient outcomes and create personalized treatment plans using machine learning and advanced AI analytics. This makes healthcare more targeted and proactive. Ultimately, it leads to improving how doctors manage care and monitor patients remotely.
Along with AI tools, cloud computing and big data play crucial roles in processing health data collected from IoT devices. Cloud computing is used to store vast amounts of information and ensure quick, secure access. Meanwhile, big data techniques manage and analyze both structured information, like test results, and unstructured data, such as doctor notes, to spot trends and enhance patient care.
A great example of these tools working together is a remote patient monitoring system. IoT devices are strategically placed in patient rooms to continuously track health metrics and environmental factors in real-time.
The system uses an advanced AI-driven audio-visual setup that monitors changes in a patient’s condition, such as abnormal body movements, potential falls, or other safety concerns. When something unusual is detected, it immediately alerts healthcare staff to facilitate a rapid response. For patients requiring constant oversight, the system acts as a virtual companion and offers ongoing support and observation.

IoT and AI in healthcare can be used for real-time patient monitoring. (Source)
Biomarkers are measurable indicators in the body, such as proteins or genes, that can help doctors detect diseases early, choose treatments, and monitor progress. They are also used to develop new drugs to treat illnesses.
The use of AI in this area of healthcare has made finding new biomarkers faster and more accurate than ever before. It works by analyzing large amounts of data and spotting patterns that humans might miss. Machine learning and deep learning models help uncover new biomarkers for diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and autoimmune disorders. This makes it possible for doctors to create more personalized treatments, improving patient outcomes and speeding up drug development.
However, it’s not always straightforward. While deep learning has improved how we analyze health data, most methods still focus on a single modality of data. Since complex diseases involve many different factors, combining multiple types of data (like genetic, protein, and metabolic data) is becoming more important for creating accurate and tailored treatments. Research shows that using AI and wearable devices in a multimodal fusion approach can help address this issue.
For instance, researchers at the University of Cambridge have used AI tools to identify biomarkers for dementia by analyzing large, complex datasets. The choice of AI method depends on the type of biomarker and the available data. For example, supervised learning is used when data comes with known labels, such as whether a patient has a disease.
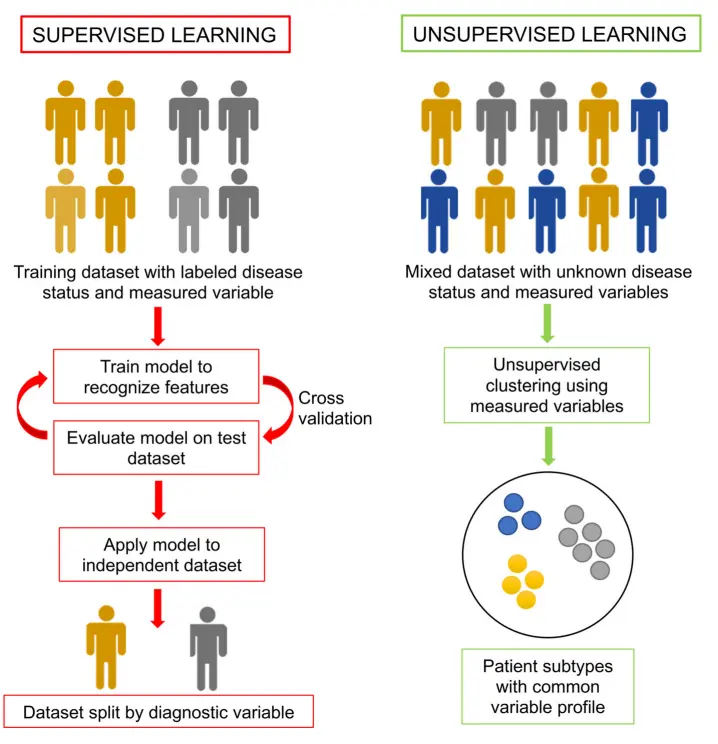
Different machine-learning methods used for finding biomarkers. (Source)
Through these techniques, AI has the potential to accelerate the discovery of dementia biomarkers. In turn, faster biomarker discovery can speed up drug development by identifying treatment targets, predicting patient responses, and reducing trial costs through more precise patient selection and monitoring.
Wearable devices can be used to track brain activity to detect stress, fatigue, and emotional changes by monitoring eye movements and sweat levels. They improve focus, learning, and performance while helping treat ADHD, PTSD, and insomnia through personalized feedback.
Using similar techniques, AI and natural language processing (NLP) can also transform speech therapy. AI can be used to analyze unclear speech and convert it into clear dialogue. This helps people with speech disorders like dysarthria and aphasia communicate more easily. AI tools with voice synthesis and visual aids are also helping children with speech issues improve pronunciation and communication skills through tailored exercises.
In fact, researchers at UC Davis Health have developed a brain-computer interface (BCI) that translates brain signals into speech with up to 97% accuracy, which is the most accurate system so far. In the study, wearable sensors were placed in the brain of a man with ALS, a condition that severely limits speech. Within minutes of activating the system, he was able to communicate his thoughts. The AI system works by detecting signals from the part of the brain that controls speech muscles. It then translates these brain signals into sounds (like syllables) and forms the words the person is trying to say.
IoT devices and AI are changing the face of how we monitor nutrition and diet by enabling real-time tracking of food intake and overall health. Everyday tools like smartwatches and fitness trackers monitor calories burned, heart rate, sleep, and activity levels, while innovative devices like smart forks and plates can track what you eat.
Similarly, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time blood sugar readings to help manage diabetes, and metabolic trackers such as breath analyzers measure how efficiently your body burns fat. Meanwhile, food tracking apps can automatically log your meals and use machine learning to suggest healthier choices.
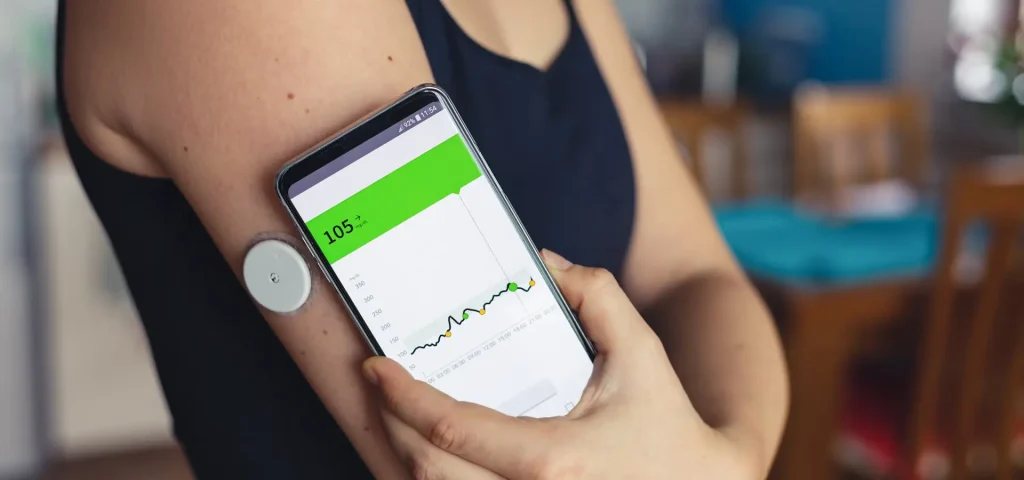

A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) device at work. (Source)
Wearable biosensors add a personalized touch by analyzing signals from your body. Smart patches and skin sensors can measure hydration, electrolyte levels, and nutrients by analyzing sweat, which helps detect vitamin and mineral deficiencies to improve diet recommendations.
For example, researchers at Texas A&M University studied how modern technology is improving diet tracking and personalized nutrition. They explored different IoT devices and AI apps that use images to track meals, biomarkers that monitor eating habits, and tools that analyze gut health and blood sugar levels. The study showed that it’s possible to create tailored diet plans for users using these tools and AI.
As you learn about AI in nutrition, you might be wondering – is it worth it? On one hand, AI can reimagine healthcare by processing huge amounts of data from wearable devices to spot trends, predict risks, and tailor treatments to individual needs. This means faster diagnoses, more accurate treatments, and overall better patient outcomes.
On the other hand, there are challenges to consider. Sensitive health data must be kept secure, and breaches are a real concern. If the data used to train AI models isn’t comprehensive or balanced, it can lead to biased or inaccurate results, which might even result in misdiagnoses. Also, while larger hospitals might afford these advanced systems, smaller healthcare facilities often struggle with the high costs and technical expertise required.
So, the answer is that it depends on the specific application, and it’s all about achieving the right balance between benefits and challenges. When implemented thoughtfully, AI can be a reliable tool in transforming patient care. However, it has to be used responsibly and with other reliable healthcare practices to truly make a difference.
Making these key decisions can be easier with technical expertise – that’s where we come in. At Objectways, we’re here to help you tap into the full potential of AI. We offer the guidance and expertise you need and can develop smart solutions that enhance patient care.
AI and wearable device technologies improve patient care through real-time health data collection, better patient monitoring, and advanced speech therapy. AI also helps discover new disease markers, leading to faster drug development and more accurate treatments. While there are challenges like data privacy, bias, and high costs, the benefits of quicker insights, better accuracy, and early disease detection show that AI and wearables are shaping the future of healthcare.
At Objectways, we provide accurate data labeling services to enhance AI performance in applications like healthcare, nutrition, and many others. We can also help you build custom AI solutions for your unique business challenges.
Eager to elevate your AI project? Reach out to us today.
