Sports have evolved a lot over the years. Players today are going beyond their coach’s training to refine their physical talent. Behind every serve, sprint, or swing, cutting-edge technologies are shaping training routines and game outcomes.
For instance, one of these key technologies is artificial intelligence (AI). Specifically, computer vision, which helps machines analyse and understand visual data, such as images or videos. In sports, computer vision is used to improve athlete training, provide fans with real-time insights, and transform how games are broadcast around the world.
Let’s say a tennis ball is flying at 120 mph. Using object tracking in computer vision, which identifies and monitors moving objects across frames, systems can precisely analyze their speed and trajectory. This technology enhances gameplay analysis, supports fair officiating, and informs better coaching decisions by providing accurate, data-driven insights.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how computer vision is used in sports, why it’s important, and some of its real-world applications. Let’s get started!
Have you ever noticed how quickly the trajectories of balls are calculated and displayed on the screen during a football or cricket match, almost immediately after they happen? This is made possible by computer vision.
In sports, computer vision systems work alongside high-speed cameras to rapidly capture and process what’s happening on the track, field, or court; all in real time. The process starts with cameras placed around the ground to record the action from multiple angles.
This recorded video or image data is then fed into computer vision and deep learning algorithms. They process the data and extract meaningful information like player position, ball trajectory, and game patterns. After processing, the data can assist referees with decisions, help coaches refine strategies, and monitor player workload to reduce the risk of injuries.
Next, let’s walk through some computer vision tasks that are widely used in sports.
These tasks or techniques make it possible for systems to perform specific objectives using sports data. Each task can break down complex visual information from sporting events into clear and meaningful insights, like using a microscope to reveal hidden details.
For example, computer vision can detect players on the field, track the ball’s movement, or recognize specific actions such as passes, jumps, or tackles. When these insights are carefully analyzed, they help players, coaches, and referees make data-driven decisions.
Here’s an overview of key computer vision tasks used in sports:
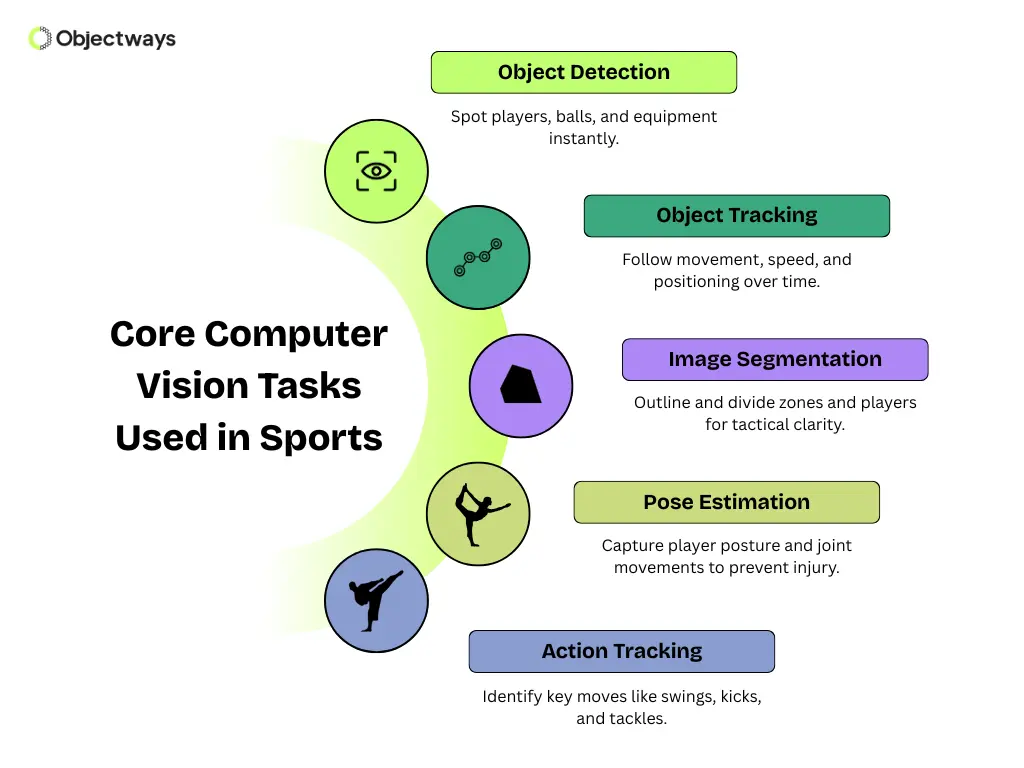
Core Computer Vision Tasks Used in Sports
So far, we’ve explored what computer vision is and the main techniques used in sports. Next, let’s look at how it’s changing various games through real-world solutions.
In professional tennis, balls travel at extremely high speeds, and the outcome of a match can depend on where they land, inside or outside the court lines. For instance, Samuel Groth, a former Australian professional tennis player, once delivered the fastest serve ever recorded at 163.4 mph (263 km/h). Most professional serves, however, average around 120 mph (190 to 200 km/h).
At such speeds, even the most eagle-eyed umpire can struggle to make accurate calls. A single misjudgment can frustrate players and fans alike and even change the course of a match.
To avoid such issues and make the game fairer, the International Tennis Federation (ITF) approved the use of Hawk-Eye, a computer vision-powered officiating system. Using advanced object tracking and multi-camera triangulation, Hawk-Eye tracks the ball in real time and reconstructs its 3D trajectory with millimeter-level accuracy.
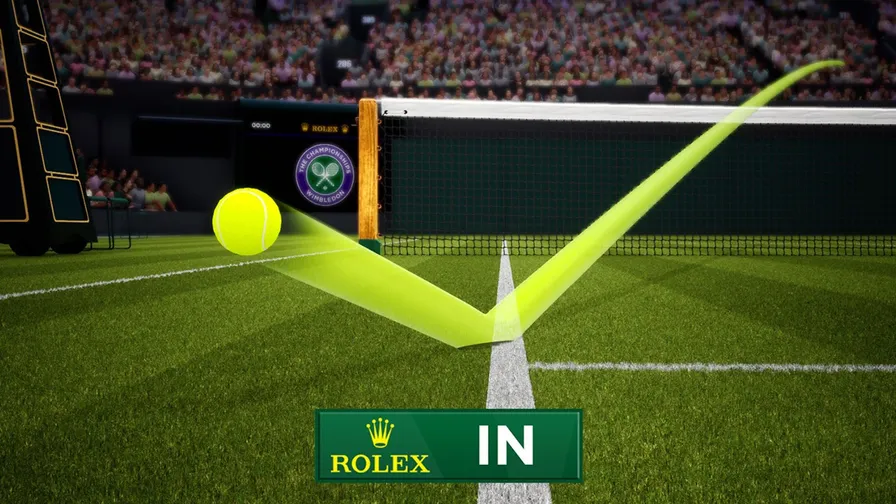
Hawk-Eye Being Used at Wimbledon 2024 (Source)
With the introduction of Hawk-Eye Live, the number of on-court officials has been reduced from ten (a chair umpire and nine line judges) to just one chair umpire at many professional tournaments, including the U.S. Open and Australian Open.
Players also gained the right to challenge calls, while fans enjoy dramatic replay visuals that bring clarity and excitement to every point. Beyond officiating, Hawk-Eye data helps coaches and players analyze shot placement, rally patterns, and tactical decisions to improve performance.
In a team sport like football, also known as soccer, a well-planned strategy is just as important as individual talent. In crucial moments such as corners and free kicks, scoring a goal often depends on precise player positioning and coordinated tactics.
For coaches, spotting and analyzing these player placement patterns with a bird’s-eye view in real time is a massive challenge. Even minor blind spots can shift the outcome of a match.
To tackle this, Google DeepMind partnered with Liverpool FC to develop TacticAI, an artificial intelligence system that provides tactical insights for corner kicks. The system builds on tracking data captured by computer vision-based cameras and uses geometric deep learning to model relationships between players, including how they move, position themselves, and interact during set plays.
Instead of analyzing raw video, TacticAI processes structured spatial data to predict outcomes such as which player is most likely to receive the ball or whether a shot attempt will occur. It can also simulate alternative player setups and show how small tactical adjustments might influence results.
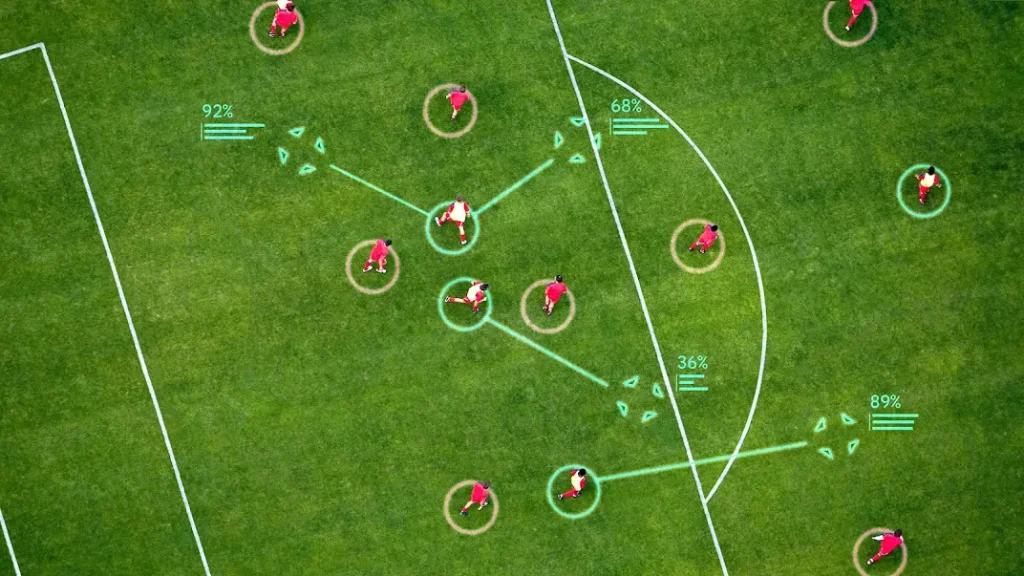
TacticAI Predicting Player Movements (Source)
In tests with Liverpool’s analysts, experts preferred TacticAI’s tactical suggestions 90% of the time over real match setups. The system can even create what-if scenarios, such as repositioning defenders to reduce the chance of a shot, helping coaches refine strategies more effectively.
TacticAI showcases how data derived from computer vision can power advanced AI tools that assist human decision-making in complex team environments like football, combining analytical precision with coaching intuition.
Athletes constantly push their physical limits, and in high-contact sports like American football, maintaining player safety is just as important as performance. Each NFL season, players are at risk of strains, concussions, joint injuries, and even severe dislocations that can cause long-term damage and cost teams significantly in medical care. Traditional monitoring methods have often struggled to flag these risks early enough to prevent them.
To improve safety, the NFL partnered with AWS to build the Digital Athlete, an AI system that combines simulation, machine learning, and video analysis. It integrates data from game footage, Next Gen Stats (player tracking data), and sensor sources to run millions of simulated in-game scenarios and estimate injury risk. The system can also infer player positioning and motion from video, helping identify potentially harmful patterns of movement or stress.
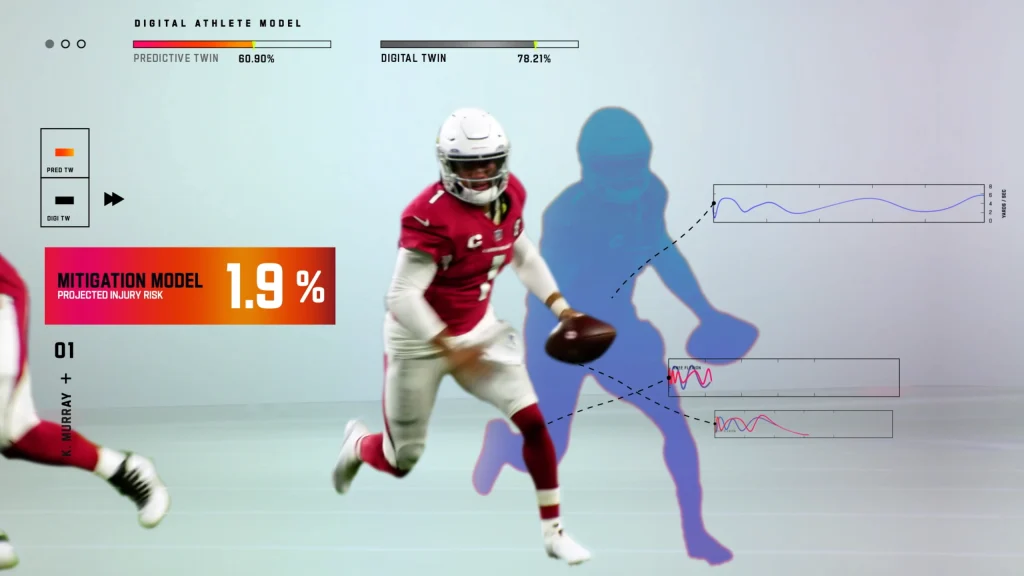
NFL’s Digital Model of a Player. (Source)
By detecting movement patterns and biomechanical risk early, the Digital Athlete supports coaches and medical teams in adjusting training loads, tailoring recovery plans, and designing safer strategies. With tools like the Digital Athlete, teams can reduce injury incidence, extend player careers, and improve overall safety in one of the world’s toughest sports.
Despite its growing use in sports, computer vision still comes with a handful of challenges that need to be considered when implementing such solutions.
Here are some limitations of computer vision in sports to keep in mind:
However, these challenges can be effectively managed. With the right expertise and partnerships, issues like data quality and privacy can be minimized.
At Objectways, we understand the challenges that come with building effective computer vision systems. As a trusted data annotation partner, we provide high-quality, accurately labeled datasets that form the foundation of reliable AI models. You can count on us to develop ethical, precise, and performance-driven computer vision solutions tailored to your business needs.
It’s likely that the future of computer vision in sports will focus on delivering real-time insights, improving athlete performance, and creating more engaging experiences for fans. Emerging computer vision trends, including live analytics, augmented reality or virtual reality integration, predictive modeling, and humanoid robots, are shedding new light on how games are played, analyzed, and enjoyed.
An interesting example is Toyota’s AI basketball robot series, which has earned two Guinness World Records. In 2019, the robot CUE sank 2020 consecutive free throws for 6.5 hours. Again in 2024, the latest model, CUE6, set the record for the farthest shot by a humanoid robot at 24.55 m (80 ft 6 in).
Using AI and computer vision, the robot calculates its position, measures the hoop’s distance, and fine-tunes its aim with millimeter-level precision. Innovations like CUE show how AI, computer vision, and robotics are redefining sports.
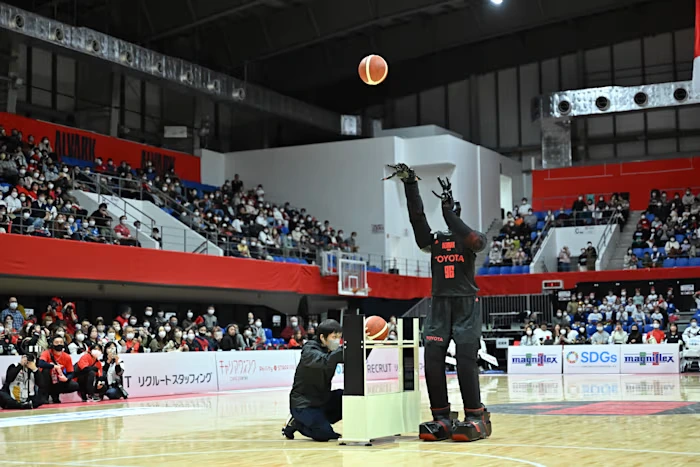

Cue6 Playing Basketball (Source)
Beyond this, we can expect computer vision to enable even more advanced applications, such as automated game analysis that delivers instant tactical insights and immersive fan experiences powered by augmented reality. As the technology continues to evolve, it will bridge the gap between data and performance, helping athletes, coaches, and fans experience sports in entirely new ways.
With real-time tracking, advanced analytics, and performance optimization, computer vision is changing how sports are played, analyzed, and experienced. In the future, it could make sports not just more competitive, but also safer, fairer, and more inclusive for everyone.
Are you ready to explore the vast potential of computer vision in sports? Get in touch with us to build scalable and ethical solutions that put your business ahead of the AI curve.
