Factories used to run with people and machines working together, guided by fixed schedules, checklists, and workers’ experience. When something went wrong, teams would step in and fix it manually – usually after the problem had already caused some damage. Most decisions were based on what had already happened, not what was coming next.
But today, that’s starting to change. More manufacturers are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to prevent problems before they happen. With the help of Internet of Things (IoT) and edge devices, factory machines are no longer just pieces of equipment – they’ve become connected, intelligent systems that learn from data. These systems can automate tasks, spot issues early, and help keep production running smoothly.
This evolution is part of a broader movement known as Industry 4.0, which brings AI and IoT to factories. By working together, these technologies create safer, faster, and more efficient production environments. The impact of such technologies in manufacturing is substantial. Studies estimate that AI could add up to 15.7 trillion dollars to the world economy by 2030.
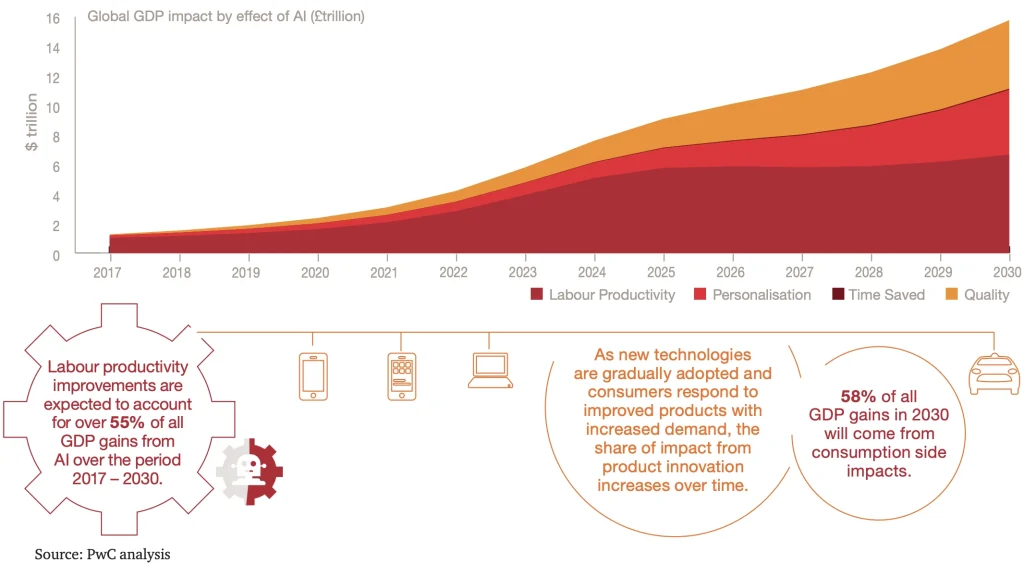
AI’s Impact on Global GDP (Source)
In this article, we’ll explore how factories are using AI tools across the production process as part of the shift toward smart manufacturing. We’ll also look at how companies can apply AI to improve operations and stay competitive.
When it comes to car manufacturing, assembly lines are the heart of production. Even minor issues can lead to major delays and increased costs. In the past, factories relied on routine inspections or waited until equipment failed before taking action. While this approach kept things running, it often resulted in costly downtime and inefficiencies.
Nowadays, many factories are using AI for predictive maintenance, a method that can help identify potential equipment issues before they lead to failure. These systems use machine learning algorithms to analyze data from IoT sensors installed in equipment.
They collect data related to the vibration, temperature, and motor speed of the machines. AI models analyze this data for patterns that may show early signs of wear, damage, or failure, subtle indicators a human might overlook. When the model detects something unusual, maintenance teams are alerted, allowing them to address the issue before it becomes a serious problem.
An interesting example of this can be seen at BMW’s Regensburg plant in Germany. The factory uses an AI system to monitor the conveyor belts that move cars through the production line. These systems analyze the data collected by IoT sensors to recognize patterns that indicate issues that usually happen before a failure.
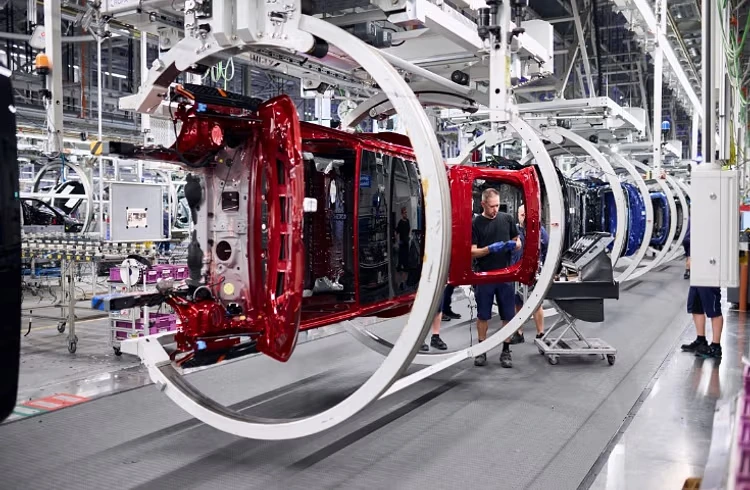

An Assembly Line at BMW’s Regensburg Plant. (Source)
When it finds something unusual, it sends a warning so that maintenance can be done before a breakdown happens. Over time, the system becomes more accurate as it learns from new data. By using this approach, the BMW plant has avoided more than 500 minutes of downtime each year.
Energy is one of the most overlooked costs in manufacturing, like a dripping faucet, which seems minor but would still add up when the water bill comes around. Small inefficiencies, such as machines running idly, equipment left on during breaks, or power-intensive tasks scheduled at peak times, can silently drain massive amounts of energy. This hidden waste drives up costs and undermines both sustainability and long-term operational efficiency.
To solve this, many factories are using AI and IoT to monitor and manage energy use in smarter ways. IoT devices, such as connected sensors and meters, are placed across machines and systems to track and collect data on energy consumption in real-time. AI models then analyze this data to identify patterns, find areas of waste, and predict future energy needs. Instead of relying on fixed schedules or manual checks, the system can adjust energy use automatically and suggest optimizations.
For instance, Schneider Electric’s smart factory is a good example of this approach. The company uses an IoT platform that connects devices, collects live operational data, and applies AI to manage performance.

Using AI and IoT to analyze real-time energy data from the production line. (Source)
With this platform, they continuously monitor how energy flows through the facility and make real-time adjustments, such as shutting down idle machines or shifting tasks to off-peak hours. The use of AI and IoT in manufacturing has helped the company reduce energy waste, improve uptime, and make steady progress toward its goal of reaching net-zero operations by 2030.
Maintaining high-quality standards is crucial in manufacturing, where even minor defects can drive up costs and lead to negative customer feedback. It’s like building a complex machine with one faulty bolt – no matter how well everything else is made, that single flaw can cause the whole system to fail.
Many factories still rely on human inspectors for quality checks, but even experienced eyes can miss subtle defects, especially during long shifts or when inspecting high volumes. To improve both accuracy and efficiency, many manufacturers are adopting AI-powered inspection systems.
These systems use IoT devices and computer vision to inspect products in detail, detecting issues like scratches, dents, incorrect dimensions, or missing components. Unlike human inspectors, AI systems can operate continuously without fatigue, ensuring consistent, around-the-clock quality control.
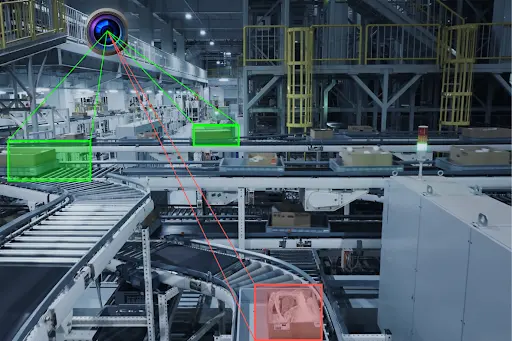
Ai Visual Inspection System Identifying Defective Products On The Production Line. (Source)
Before any component is made in a factory, it typically begins as a 3D model. These models created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, define every detail – holes, edges, and shapes – that the final part will have.
To turn those designs into physical objects, machines like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) tools need to understand the features in the 3D model. That means the features need to be labeled correctly so the machines know where to cut, drill, or shape the material with precision.
Traditionally, engineers have done this labeling manually. However, when components have complex shapes, the process can take hours and is prone to human error. Today, AI is being used to automatically identify and label features in 3D CAD models.
A recent study found that AI models trained on hundreds of designs can learn to recognize common features, like holes and pockets, by analyzing their shape and position. The AI system can interpret the geometry, understand the function of each section, and apply the correct labels faster and more accurately than a human.
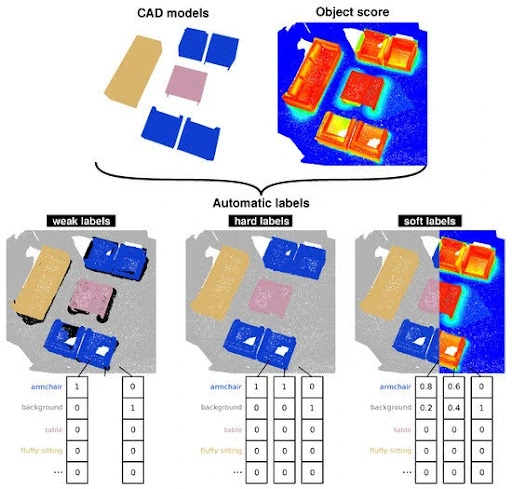
Examples of AI labels used by 3D CAD models to recognize features and assign categories. (Source)
This automation makes it easier to prepare models for manufacturing, reduces errors, and shortens the time between design and production. In high-mix or custom manufacturing, where components frequently change, AI-powered labeling saves time and improves consistency across the production process.
AI has a lot to offer in manufacturing, but using it in real factory settings isn’t always easy. Many companies start with successful pilot projects but run into problems when they try to scale or keep them running. Here are some common challenges manufacturers face:
Bringing AI into manufacturing isn’t just about using the latest technology – it also requires the right data, careful setup, and proper model training. Many manufacturers face delays because they lack the time, tools, or in-house expertise to manage these steps on their own.
Objectways can help bridge that gap. We specialize in providing high-quality data that AI systems need to perform effectively. With a skilled team of annotators and technical experts, Objectways handles tasks like labeling product images, annotating 3D models, and organizing sensor data. This makes it easier for factories to train AI systems that detect defects, monitor equipment, and support automation.
The best part is our support doesn’t stop at data. Objectways also offers AI development services and works closely with factory teams to ensure AI tools connect smoothly with existing systems. We understand how factory operations run and help reduce the time, cost, and risk of getting new AI solutions up and running.
AI can help factories reduce downtime, improve product quality, and use energy more efficiently. However, AI solutions are heavily dependent on clear, well-prepared data. That means labeling images, annotating sensor logs, and organizing 3D models in a way machines can interpret and learn from.
Also, different factories have different needs – some require speed, and others demand precision. However, no matter the objective, high-quality data is what powers successful AI projects.
At Objectways, we help manufacturers transform their factories. Our team delivers accurate data labeling and sourcing services that support real-world AI projects on the factory floor. If you’re planning to integrate AI into your operations, contact us to get started today!
