With innovations like ChatGPT gaining in popularity, artificial intelligence (AI) is now a part of daily life for millions of people worldwide. It is used in sectors like healthcare, transportation, customer service, education, and even entertainment. As these systems become more common, they also bring up hard-to-ignore risks. Unfortunately, AI models can make decisions that reflect bias, invade privacy, or create safety concerns.
From interactive chatbots to the warnings seen in films like ‘The Terminator,’ artificial intelligence has always raised questions about control and consequences. These issues have sparked a larger public debate: is AI good or bad, and how do we make sure it helps society rather than harms it? In fact, a recent survey found that 71% of business leaders believe AI cannot be trusted without stronger AI governance in place.
Even when designed with good intentions, AI systems can still produce harmful outcomes. These consequences are real and can affect people in everyday situations. That is why AI governance is no longer a suggestion or recommendation. It is critical to ensure that AI is used responsibly, lawfully, and in ways that protect public interests.
In this article, we’ll explore three key areas of AI governance: creating clear AI policies, building transparent systems, and protecting the public from disinformation. Let’s dive in!
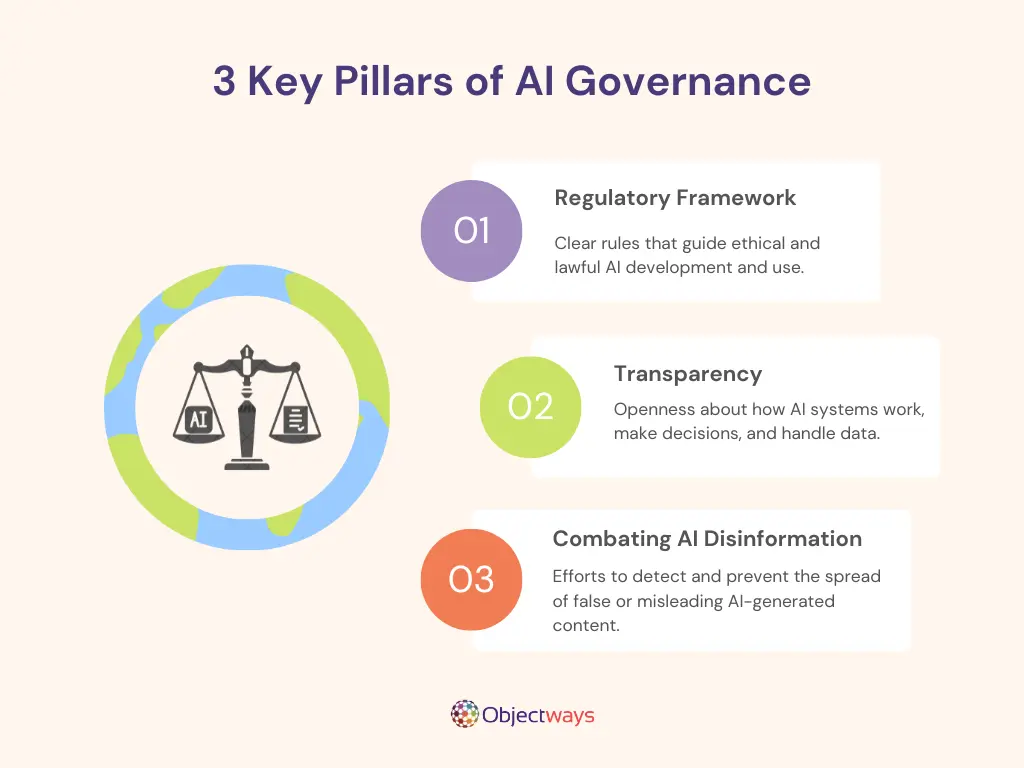
The Three Core Pillars of AI Governance
AI has moved quickly from research labs to everyday applications across various industries and services. AI innovations are now helping with tasks like screening job candidates, scoring credit applications, guiding policing systems, and influencing what content people see online.
These tools rely on models trained using large amounts of data. The accuracy and fairness of an AI model depend heavily on the quality of its training data. If the training data includes bias or gaps, those issues often carry over into the system’s decisions.
While AI tools offer convenience and efficiency, they also raise serious ethical concerns. You can think of AI models as a mirror. They reflect what they learn, even when that reflection is unfair. If the data is biased, the outcome will likely be biased too.
For example, in 2018, Amazon shut down its internal AI hiring tool after it showed bias against women. The system had learned from historical data that favored male applicants. Similarly, facial recognition software used in law enforcement has faced issues related to bias.
In 2020, Robert Williams, a Black man from Detroit, was wrongfully arrested after facial recognition software misidentified him as a robbery suspect. Despite clear differences between Williams and the actual suspect, the software’s error led to a traumatic experience for him and his family.
These incidents showcase how unregulated AI solutions can produce real-world harm. They also erode public trust in new technologies and increase skepticism about whether AI is good or bad.
AI isn’t so different from a fast-moving vehicle. Without a clear road and working brakes, it can cause harm. Regulations can act as a road map and control system. They help guide AI development toward safe and responsible use that reflects public values and legal standards.
For instance, without regulations, smart home devices powered by AI can pick up private conversations without warning. Likewise, in customer service, automated systems have denied refunds or blocked accounts based on errors in the data. These examples may seem small, but they can affect daily life in serious ways. They are good reminders of why AI systems need proper checks before being widely used.
As AI adoption grows, governments around the world are introducing new laws to guide its development and use. These AI policies are designed to reduce risk while encouraging innovation.
Here are some examples of key AI regulations being put in place around the world:

A Look at EU AI Act Risk Categories (Source)
Another issue associated with AI is transparency. As these systems are used to make important decisions in healthcare, education, and finance, people are asking: How do these systems reach their conclusions, and can we trust the results?
Transparency helps answer those concerns. People are more likely to trust AI innovations when they understand how it works. When the decision-making process is hidden, even accurate results can feel suspicious.
One way to improve trust in AI is through explainable AI (XAI), which is a technology that clearly shows how decisions are made. By revealing the reasoning behind outcomes, XAI facilitates accountability and supports stronger AI compliance.
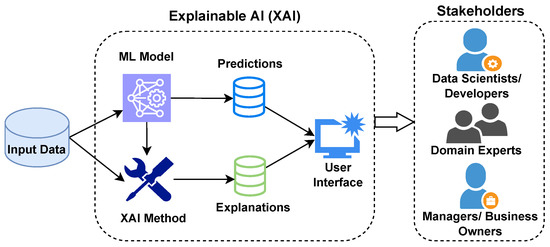
How Explainable AI Delivers Insights to Users (Source)
In the same way, model cards are impactful tools that can make AI models more transparent. They’re short documents that explain what a model was trained to do, what data it used, and where it might fall short. A good example is the documentation released by OpenAI for its GPT-4 and GPT-4-turbo (o3) models, which outlines their training goals, capabilities, and known limitations.
However, transparency isn’t always easy to achieve. Complex systems, such as large language models, can be difficult to explain – even for experts. Despite these challenges, investing in transparency is vital for building trust and promoting responsible AI.
In recent years, AI has made it easier to create false information that looks and sounds real. Sometimes, AI tools are used in coordinated disinformation campaigns to influence public opinion, spread rumors, and mislead people.
Alongside this, the rise of deepfakes is a growing concern. Deepfakes are fake images, videos, or audio clips that show people doing or saying things they never did. In early 2024, a deepfake audio clip a U.S. presidential candidate went viral just before a major election. It spread quickly across social media before it was flagged and taken down.
Tackling this type of issue isn’t simple. AI-generated content spreads fast, is often convincing, and can be difficult to detect in time to prevent harm.
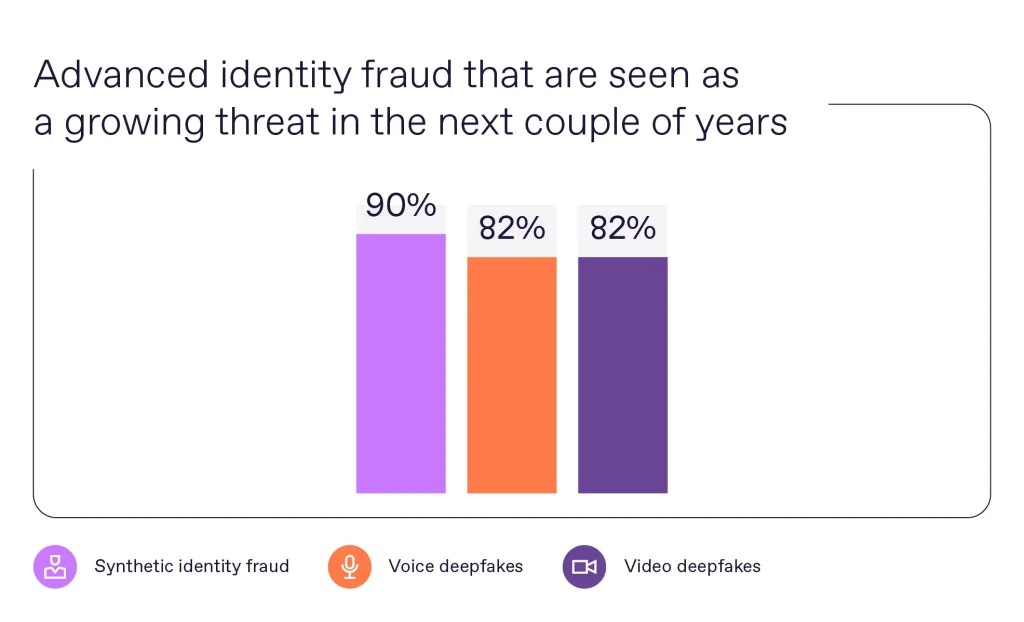
Emerging Threats Related to Identity Fraud (Source)
In response, developers are building tools that find patterns in speech, image details, and writing styles to identify what is fake. Content moderation plays a crucial role here. These systems help platforms review posts, remove harmful content, and reduce the reach of false information.
Many organizations are taking active steps to manage the risks and responsibilities that come with using AI. Here are some common practices organizations are using to promote responsible AI development:
Companies like Objectways can help put these best practices into action. If you’re looking for AI experts to support governance, ensure data quality, or improve model transparency, Objectways offers the tools and experience to empower you to build responsible, compliant AI systems.
Whether you’re just getting started or scaling up, partnering with the right team can make all the difference.
While AI regulation is important, it also needs to allow room for innovation. A strong AI policy does both: it protects people while giving researchers and companies the freedom to keep improving and solving real-world problems.
Take Singapore’s Model AI Governance Framework, for example, which provides organizations with clear guidance on ethically implementing AI. It focuses on principles like transparency, accountability, human-centricity, and XAI.
Along the same lines, Canada’s Algorithmic Impact Assessment tool acts as a diagnostic checklist. It supports public sector teams in evaluating the potential risks and impacts of automated decision systems before deployment. By assessing factors like data quality, fairness, and privacy, the tool promotes responsible AI.
Going a step further, Google’s People + AI Research (PAIR) initiative focuses on reducing the gap between complex AI systems and the people who use them. The team builds open-source tools and research to make AI easier to understand, more accurate, and more useful. The goal is to create AI systems that support human values and build trust.
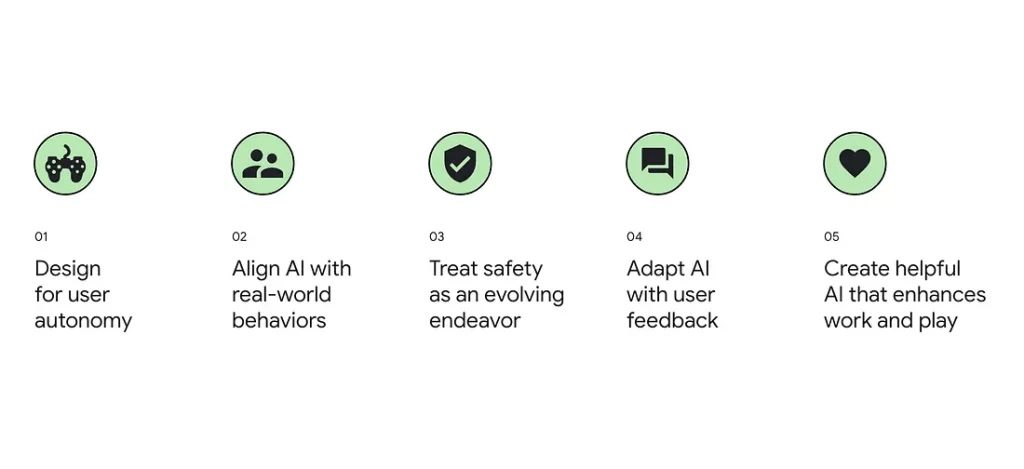
Key Principles From Google’s PAIR Initiative (Source)
Responsible AI development relies on AI governance that promotes safety, fairness, and public trust. Clear and consistent AI policies make it possible for organizations to create systems that meet ethical standards while solving real-world problems.
However, AI regulation alone isn’t enough. People also need transparency built into AI systems to understand how they work and why they make certain decisions. Accountability should be integrated at every stage of development and deployment.
At Objectways, we support the development of ethical AI through high-quality data practices and collaborative partnerships. If you’re interested in building responsible and ethical AI solutions, book a call with our team today and see how we can build smarter, more efficient innovations together.
