Cities are a lot like living systems. With each new road, housing development, or transit line, cities grow more complex. They add new layers to essential systems like the water supply, energy distribution, transportation, and communication. However, as these systems expand and populations increase, keeping everything running smoothly becomes a serious hurdle.
Cutting-edge infrastructure generates large volumes of real-time data every day, including traffic patterns, energy demand, water flow, and waste levels. Managing this amount of information and responding to it quickly requires more than manual oversight.
To keep up with all this complexity, cities are turning to artificial intelligence (AI). It enables them to react instantaneously and optimize planning processes using data-driven insights. For example, traffic can be rerouted before it gets stuck. Similarly, leaks can be spotted before they cause damage. Meanwhile, power can be distributed more efficiently based on actual demand.
AI is also making it possible for planners to rethink how cities grow by testing different land use ideas and designing more resilient spaces. In fact, momentum is building quickly, with the global market for AI in urban planning set to reach around $9.1 billion by 2033.
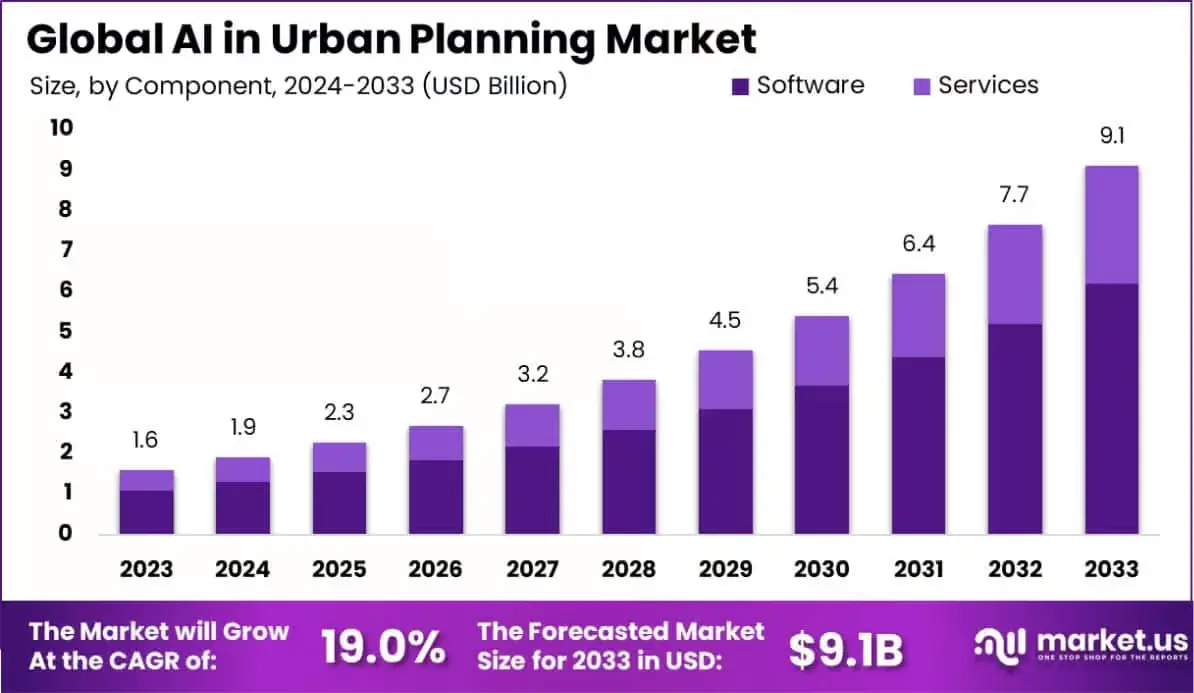
Projected Market Growth of AI in Urban Planning (Source)
In this article, we break down how smart city infrastructure powered by AI is transforming everything from traffic flow to long-term planning.
Smart infrastructure refers to physical systems like roads, utilities, and buildings being connected through digital technologies for better monitoring, operation, and maintenance. These systems use sensors, cameras, and edge devices to collect high-quality data, helping cities respond faster and use resources more efficiently.
So, how does this constant flow of information actually make a difference? The data collected by these systems plays a direct role in how infrastructure is managed and maintained. Instead of depending on scheduled checks or manual processes, smart infrastructure allows for early detection of issues, predictive maintenance, and automated decision-making. This leads to fewer disruptions, lower costs, and improved public services.
Specifically, smart infrastructure relies on a combination of technologies that work together to collect, locate, and analyze data from physical systems. These technologies enable cities to monitor infrastructure conditions in real time and respond more effectively.
Here are some of the key technologies that are used in smart city infrastructure:
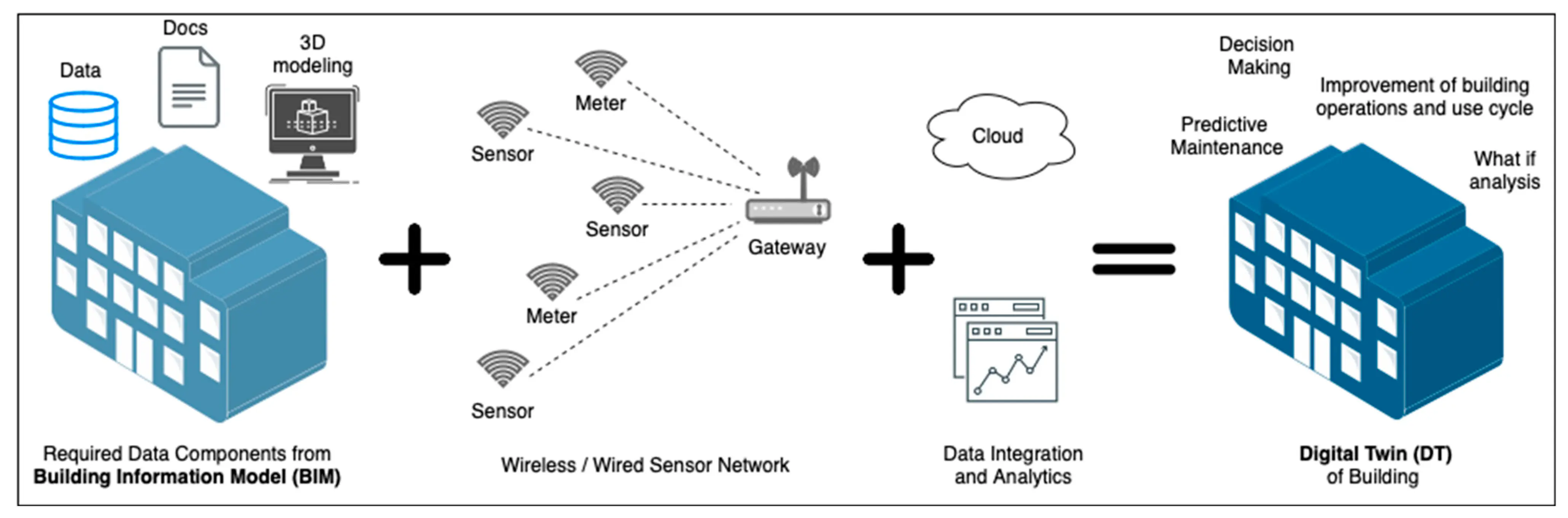
Turning Physical Buildings into Smart Systems through Connected Technologies. (Source)
Urban mobility is a critical part of how well a city functions. However, as more people and cars fill the streets, managing traffic, parking, and public transit becomes more and more challenging.
The reality is that cities need practical solutions that can handle everyday mobility and also support long-term sustainability. To handle these issues, cities are turning to AI technologies that offer real-time insights and more intelligent control over transport systems.
Several transport systems have already integrated these technologies. For instance, when it comes to parking, sensor-based systems can show where spots are available and guide drivers. This optimizes traffic and saves fuel.
Likewise, public transport systems can use AI to adjust schedules based on real-time traffic, weather, and how many people are traveling. Beyond transit schedules, AI also plays a major role in managing traffic on the roads. AI models can process GPS data, road sensor input, and historical trends to understand traffic patterns and predict congestion. This means traffic signals can adjust on their own as road conditions change.
An interesting example of AI-enabled urban mobility is Google’s Mobility AI project. It uses anonymous location data, traffic simulations, and digital models of city roads to help test and plan changes before they’re made. In Seattle, the system was able to manage traffic during major events by suggesting better routes.
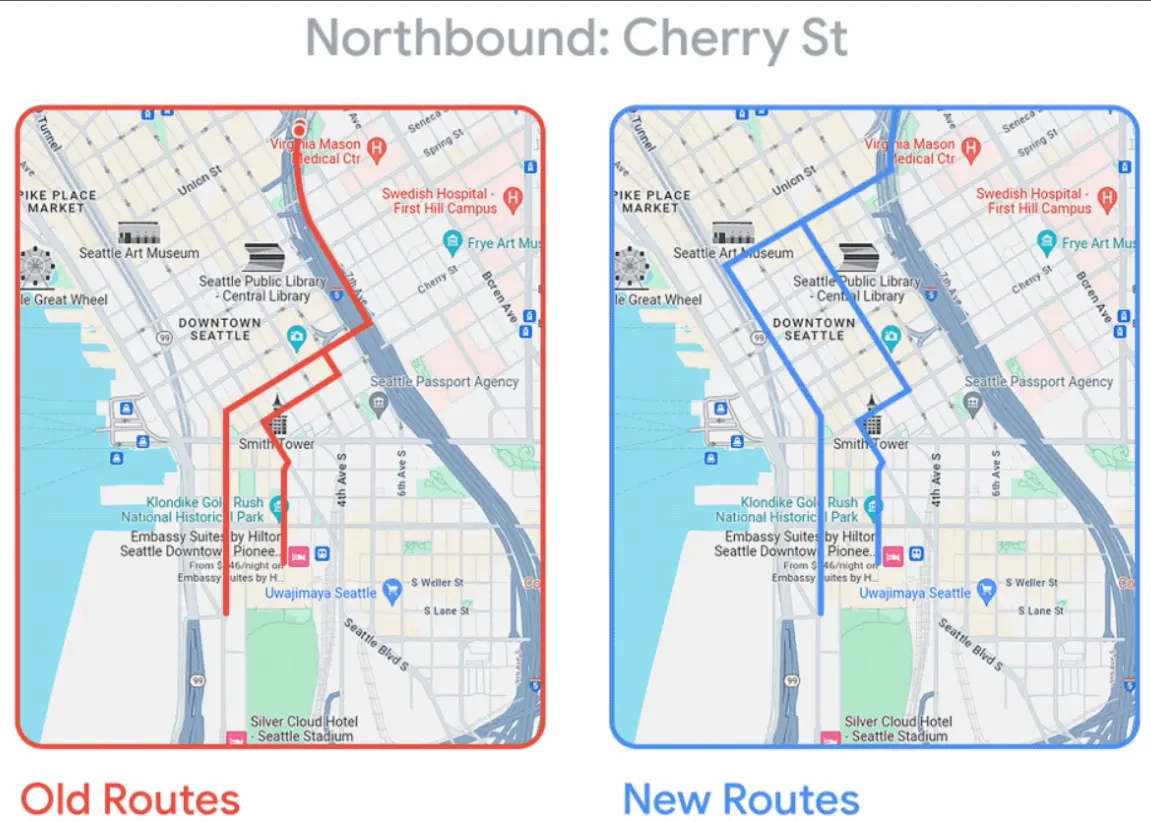
Seattle used Google’s Mobility AI project to plan better traffic routes. (Source)
Water and waste systems keep cities running, but they’re feeling the pressure. As pipes and plants age, populations grow, and climate challenges intensify, keeping these systems working smoothly has become harder and more expensive. As of 2023, nearly 4 billion people around the world live under highly water-stressed conditions for at least one month each year.
In response, many cities are adopting AI systems to make water networks more reliable. These tools use sensor data to monitor flow, track pressure levels, and analyze weather conditions. With this information, they can detect leaks, predict rising demand, and schedule maintenance before problems occur. The result is more efficient water use, more reliable service, and extended system durability.
These kinds of solutions are also being used in waste collection. Smart bins equipped with sensors and image recognition software can detect fill levels, identify waste types, and track usage patterns. This data is used to optimize pickup routes, reduce fuel consumption, and avoid overflows or unnecessary trips.

AI-powered bins automatically sort waste and guide users for smarter recycling. (Source)
So far, we’ve looked at water, waste, and roads in smart cities. But none of these systems work without energy.
The energy sector powers everything behind the scenes, and it’s far from straightforward. Demand rises and falls throughout the day, while renewables like wind and solar depend on the weather. To keep things running without missing a beat, cities are leaning on smart energy systems that can sense change and adjust automatically.
AI helps with this shift by enabling smarter energy use, improving system stability, and supporting sustainability goals. It supports grids by driving them to respond faster, use energy more efficiently, and avoid outages or waste, especially as cities grow and turn to cleaner energy sources.
Here are some key ways AI supports smarter, more reliable energy systems in cities:
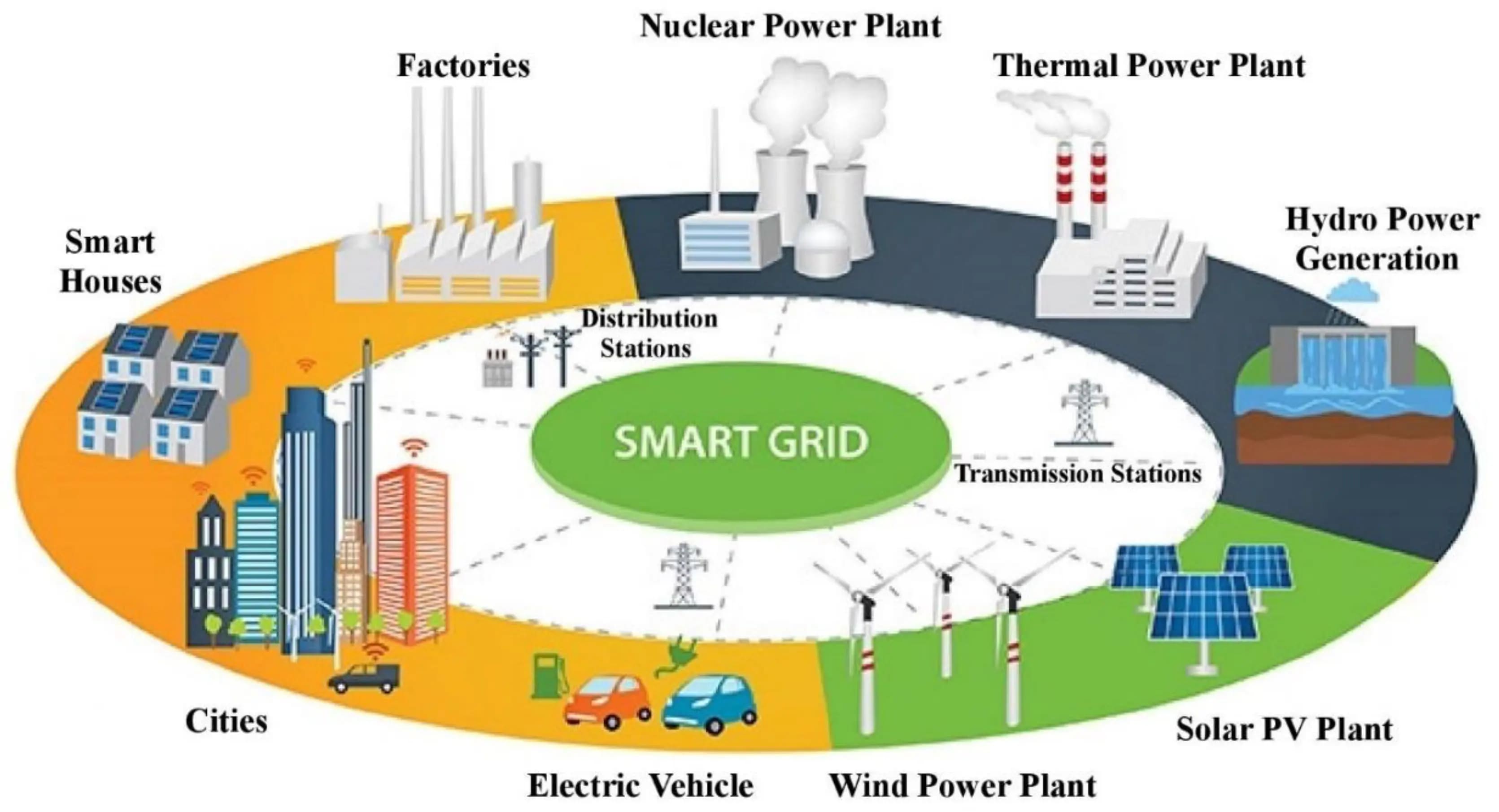
AI helps smart grids balance energy between energy sources and end users. (Source)
Emergencies like disease outbreaks, fires, and major accidents can happen without any warning. Quick responses are vital, but many cities still depend on slow, manual systems. Delays can make it harder to protect public health and reach people needing help in time.
To improve emergency response, cities are using AI to spot early warning signs and support quicker, smarter decisions. These systems pull in data from multiple sources to detect health risks and environmental threats in real time.
In the case of floods, AI can be used to analyze satellite images, weather forecasts, and sensor data to identify risks early. This allows cities to send alerts and take action before severe damage occurs.
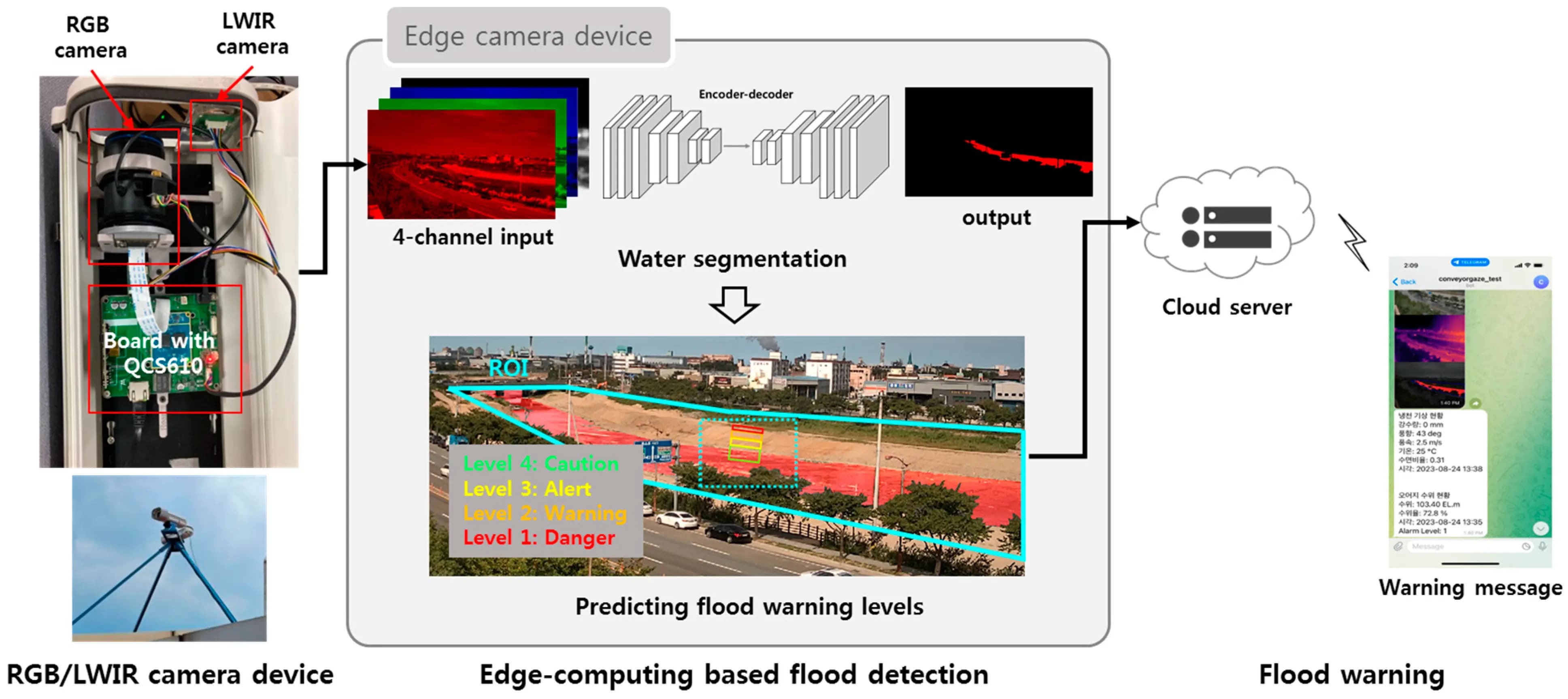
AI-driven systems can detect floods and send instant alerts. (Source)
A good example comes from Chiayi County, Taiwan. To strengthen disaster response, the region deployed a system that combines satellite imagery, environmental sensors, and 5G connectivity. It continuously monitors flood-prone and high-risk areas, helping officials detect early signs of flooding or landslides.
There’s always something changing in a city. Roads are rerouted, buildings rise higher, and old neighborhoods evolve into new ones. But with so many moving parts, planning for growth while maintaining balance between housing, transport, green space, and sustainability isn’t easy.
One way AI is helping navigate this complexity is through zoning optimization. Rather than using fixed templates, planners can feed AI models with variables like land value, energy efficiency, sunlight exposure, and traffic flow. In return, the system suggests how different land uses, such as residential, commercial, or public, could be arranged to make better use of space and resources.
Another impactful concept is the digital twin. It is a real-time 3D model of an entire city that updates with live data. Planners use it to simulate how new buildings, roads, or policy changes could affect traffic flow, energy use, or public access. These models can also identify underserved areas by analyzing demographic trends and infrastructure gaps, supporting more equitable decisions around where to add clinics, parks, or transit options.
AI is empowering cities to respond faster, use fewer resources, and involve citizens in smarter ways. Here are some of the key improvements it brings to everyday urban services:
Despite the promise of AI, cities still need to consider a few key hurdles before these systems can be scaled widely:
Cities are evolving and are becoming more connected and responsive to the needs of the people who live in them. AI plays a growing role in making this possible, powering everything from emergency systems and energy grids to public planning and real-time mobility.
At Objectways, we support this future by delivering accurate data labeling services that strengthen AI systems in areas like urban mobility, energy, public safety, and planning. Our expertise helps teams build smarter, more reliable AI models that perform well in real-world conditions.
Ready to make your city smarter with AI? Get in touch with us today.
