A doctor can end up reviewing dozens of medical scans in a single day. Some are routine and easy to move through. Others take much longer. Two scans can look almost identical at first, yet one small detail can lead to a completely different diagnosis.
In other words, medical data isn’t uniform or simple. Imaging results differ from patient to patient and vary based on the equipment used and the condition being examined. Clinical reports also follow different structures depending on hospitals, departments, and workflows.
These variations aren’t just noise. They provide clinicians with the crucial context needed to understand what is occurring within a patient’s body.
However, things get tricky as this information grows. Healthcare systems are now generating enormous amounts of medical data every day. Reviewing images, reports, and records requires focus and time, especially when decisions affect patient care. Traditional processes simply weren’t built to handle this volume consistently.
To support clinicians, healthcare systems are increasingly relying on artificial intelligence. Medical AI helps analyze scans, assist with diagnoses, and support clinical decisions. But before AI models can be used safely, they must learn how to interpret medical data accurately.
Medical data annotation makes that possible. By carefully labeling medical images and records, annotation teaches AI systems to recognize structures, findings, and conditions. High-quality annotation supports accurate predictions and reliable clinical tools. Poor annotation leads to errors that can affect patient outcomes.
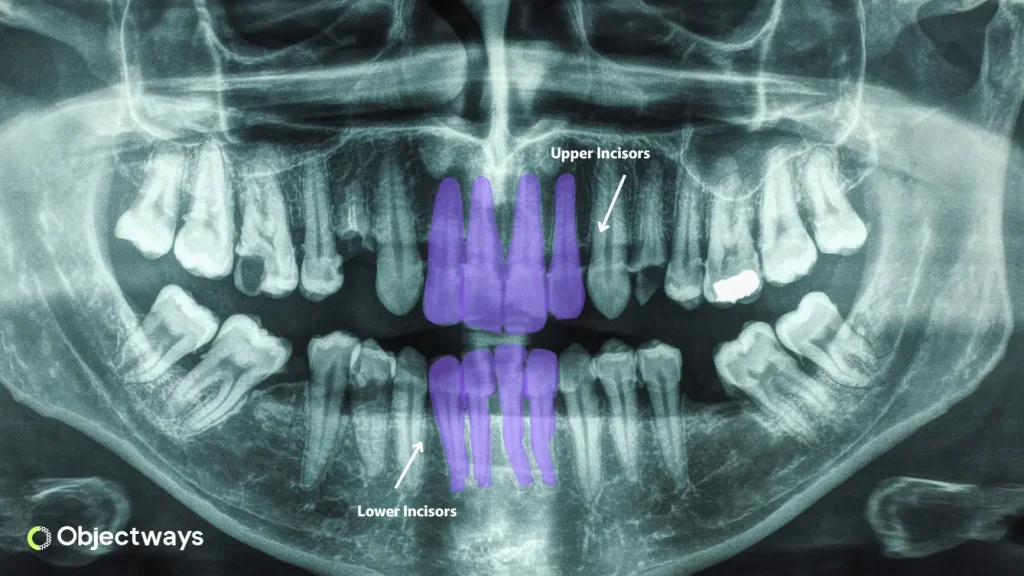
An Example of Medical Data Annotation
In this article, we’ll explore how medical data annotation supports medical AI and why precision matters in real clinical settings. Let’s get started!
Medical AI refers to the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze complex medical data and support clinical work. Since most of this data is visual, AI systems rely on computer vision to interpret medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
Computer vision enables machines to understand visual information by learning from annotated medical images. During training, vision models are exposed to large volumes of labeled data that teach them how to recognize patterns, structures, and abnormalities. Once trained, these models can assist with tasks that would otherwise take clinicians significant time and effort.
Today, vision-based AI systems are used across healthcare in several important ways. Here’s a glimpse at how they are making an impact:
Medical data annotation is the process of adding informative labels to medical data so AI models can learn from it. In simple terms, annotation helps machines understand what they are seeing and learn to recognize meaningful patterns.
For example, labels may mark the boundaries of a tumor or define the shape of an organ within a scan. This guided learning lets AI systems perform tasks more accurately when used in clinical settings.
In medical image annotation, small details matter, since even slight differences in position or shape can influence how a condition is interpreted. Because of this, medical data annotation is more complex than general data labeling. Precision and consistency are essential throughout the process, as errors or inconsistencies can affect how models learn and make predictions.
At the same time, annotation has to be carried out with strict attention to patient privacy. Medical data labeling takes place under regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR, which define how data can be accessed, processed, and stored. Annotation teams generally follow structured protocols to protect patient information while keeping the data usable for training.
Simply put, effective medical data annotation requires domain expertise, careful attention to detail, and adherence to regulatory standards to support reliable medical AI systems.
To train AI models well, every piece of medical data needs to be clearly labeled. Next, let’s take a look at the different types of medical annotation used in hospitals and clinics.
Medical images make up a large portion of healthcare data. For this type of data, experts label regions such as fractures, tumors, bleeding, or organ boundaries.
Many health systems now use such vision-based AI tools that scan imaging data as it is captured. These systems can flag urgent findings, such as internal bleeding or lung nodules, so that radiologists can review them quickly.
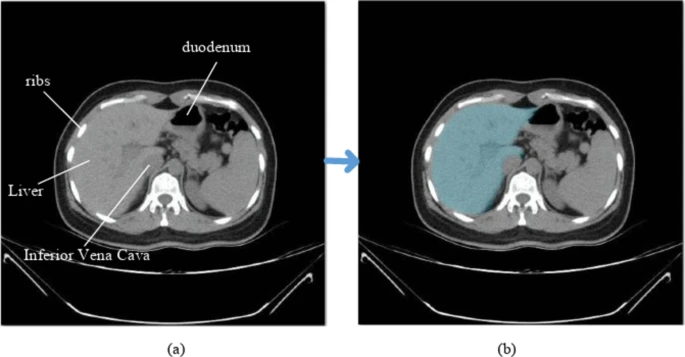
A Look at Liver Segmentation (Source)
Medical annotation isn’t limited to flat images. CT and MRI scans often produce three-dimensional data, in which structures have to be labeled across multiple slices.
Annotated 3D scans help AI models support earlier cancer detection and more accurate assessments. For instance, in some hospitals, models trained on labeled kidney CT scans are being used to assist radiologists in identifying tumors and help surgeons plan procedures more efficiently.
Beyond images, AI systems are also trained on annotated clinical notes and electronic health records. When this data is labeled correctly, predictive models can identify patients at higher risk of complications or alert care teams earlier. For example, hospitals use AI tools trained on imaging data combined with patient records to flag urgent findings and support faster clinical decisions.
Hospitals also rely on lab reports, vital signs, and monitoring data that evolve over time. Annotating this data involves labeling values, trends, and outcomes so AI systems can learn how changes relate to patient health.
Models trained on annotated time series data can detect early signs of deterioration, such as gradual shifts in lab values or vital signs. This makes it possible for clinicians to intervene earlier and reduce the need for emergency responses.
In radiology, annotation supports AI systems that review large volumes of scans each day. These models are trained on thousands of annotated cases, which helps them highlight potential abnormalities and areas that require closer review.
As a result, radiologists can spend less time on routine scans and focus more on complex cases and clinical judgment. AI supports efficiency and prioritization while keeping decision-making in the hands of clinicians.
Now that we have a better understanding of how medical data annotation supports AI systems, let’s see how AI shows up in real hospital settings.
Radiology departments are among the busiest areas in healthcare. Every day, radiologists review large volumes of scans under tight time constraints. In this setting, subtle findings can be difficult to catch consistently, especially when workloads are high.
AI-based radiology tools are designed to support this process. These systems analyze incoming scans and draw attention to regions that may need closer review, such as unusual tissue patterns or unclear boundaries. When integrated into hospital workflows, this enables teams to manage imaging data better. Urgent scans can be reviewed sooner, routine cases move through the system faster, and reporting becomes more consistent across patients.
The effectiveness of these tools depends heavily on how well they were trained. Studies show that systems trained on accurately annotated medical images are better at recognizing clinically meaningful patterns.
To detect cancer early, doctors need to clearly see where a tumor is located and how it spreads. This information guides diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical decisions. Even small differences in size or position can change how a patient is treated.
AI-based vision systems are now being used to support this process. These models analyze medical images and highlight regions that may contain abnormal tissue, helping clinicians focus their attention where it is needed most.
To work accurately, these systems are trained on large datasets of annotated medical images. Specialists carefully outline tumor regions and label different tissue types so models can learn how cancer appears across scans. These datasets often include thousands of pathology slides and medical images.
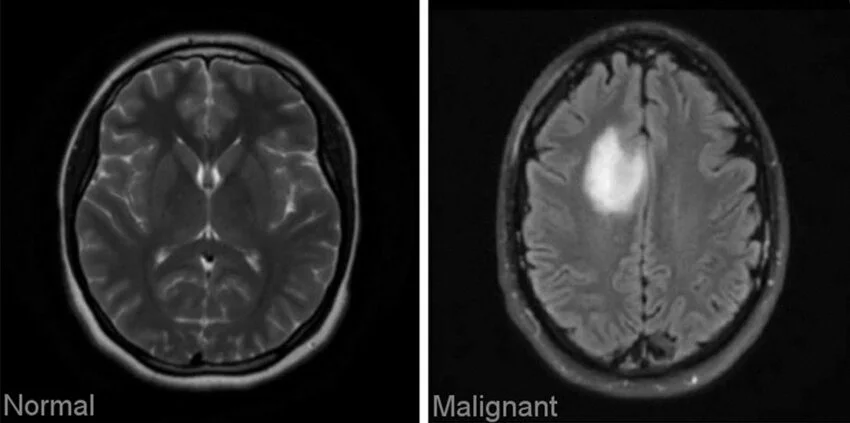
Sample Images from a Dataset of Brain Tumors (Source)
A recent example comes from researchers at Harvard Medical School, who trained an AI system using annotated digital pathology slides from multiple cancer types. The model learned to detect cancer cells, predict a tumor’s molecular profile, and estimate patient survival by analyzing visible cellular features.
It also identified patterns in the tissue surrounding tumors that relate to how patients respond to treatment. This level of performance was made possible through precise and consistent tumor annotation.
Keeping track of patient conversations is important, but manually taking notes can be time‑consuming and distracting. AI tools are being used to record doctor-patient interactions and automatically capture key details.
Interestingly, in a recent study, AI tools that capture conversations between doctors and patients were found to save a lot of time. Such systems can turn spoken conversations into structured notes that clinicians can quickly review and finalize for the patient record.
These tools often integrate directly with EHR workflows, which makes documentation faster, less stressful, and more seamless as part of a clinician’s day. To do so accurately, such models are trained on carefully annotated clinical conversations so they can recognize medical terms, context, and the flow of a consultation.
Many serious complications don’t appear suddenly. There are often early warning signs before a patient’s condition worsens. Tracking these subtle changes across multiple patients, however, can be time-consuming. The real challenge is spotting these signals early enough to act.
Predictive risk analysis tools powered by AI are designed to do exactly that. These systems analyze medical images, patient history, lab results, and ongoing clinical data to detect patterns that point to a higher risk of deterioration.
For example, recent research shows that advanced AI models can estimate cardiovascular risk directly from routine CT scans, without the need for extra tests. This approach could make identifying cardiovascular risk less expensive and less invasive, while helping clinicians spot early warning signs sooner. The accuracy of these predictions depends heavily on how well medical data is labeled during training.
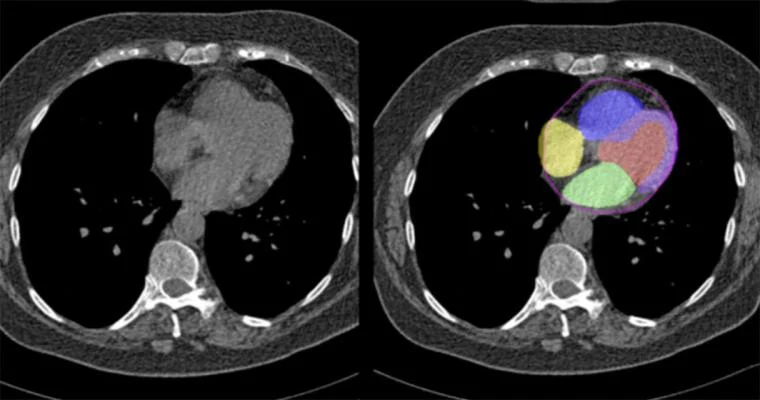
Trained AI Models Evaluating Cardiovascular Risk Using CT Scan Data (Source)
Researching and developing medicines is a lengthy process. Scientists first study how a disease behaves in the body, then test thousands of compounds to find potential treatments. This early discovery phase alone can take years.
To move faster, researchers are now using AI-driven systems that analyze large volumes of biological, chemical, and clinical data. These tools scan lab results, molecular structures, and genetic data to spot patterns that point to promising drug candidates worth testing further.
This shift toward data-driven discovery has also been recognized by regulators. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has published guidance on the responsible use of AI across different stages of drug development, encouraging innovation while maintaining safety and reliability.
So far, we’ve talked about why medical data annotation matters. The next question is, who actually does this work?
A medical annotator does more than mark images or label reports. Their role is to organize complex medical information so AI systems can learn from it accurately.
You can think of a medical annotator as a guide who helps AI navigate medical data. Just as a guide points out important landmarks on a map, medical annotators highlight critical details in scans, reports, and records so the model knows what to focus on.
Their daily work includes reviewing radiology images, pathology slides, and clinical notes, then carefully labeling structures, abnormalities, and disease patterns. Each label is added with an understanding of how the model will use that information during training and real-world deployment.
A medical annotator applies medical knowledge to structured data labeling.
Unlike general data annotation, medical annotation requires strong domain knowledge. Understanding anatomy, medical terminology, and clinical context is essential. Even a small labeling error can influence how an AI system performs in patient care settings.
That’s why many medical annotation tasks are handled by professionals with clinical training or strong medical backgrounds. Their expertise ensures consistency, accuracy, and reliability across large datasets, which directly shapes how safely and effectively medical AI systems perform.
While data annotation is essential for training medical AI, doing it right is far from simple. Here are some challenges involved:
Reliable medical AI solutions depend on the quality of the data used to train AI models. This is where working with an experienced medical annotation provider makes a real difference.
Teams with hands-on healthcare experience understand both sides of data annotation: the clinical context and the technical requirements of AI models. For instance, at Objectways, we specialize in data annotation for AI systems across complex domains, with over seven years of experience supporting healthcare-focused projects.
We help teams build dependable medical AI systems by preparing accurate, well-structured datasets that reflect real clinical scenarios. Our trained annotators follow clear guidelines and strict quality checks to ensure consistency across large volumes of medical data.
In particular, our medical annotation workflows are designed around real clinical use cases and healthcare standards. This ensures the data remains both usable for AI training and safe for patient care.
By carefully managing this foundation, we enable healthcare organizations to develop AI solutions that are reliable, scalable, and ready for real-world medical environments.
Medical AI relies on precise data. When data annotations are unreliable, even the most advanced models struggle to deliver results that can be trusted in real clinical settings. Working with teams that understand medical data, follow strict processes, and prioritize quality helps reduce risk and improve model performance from the start.
Objectways specialises in data annotation that supports real-world use cases. If you’re building a new system or scaling an existing one, book a call with Objectways to explore scalable annotation solutions.
